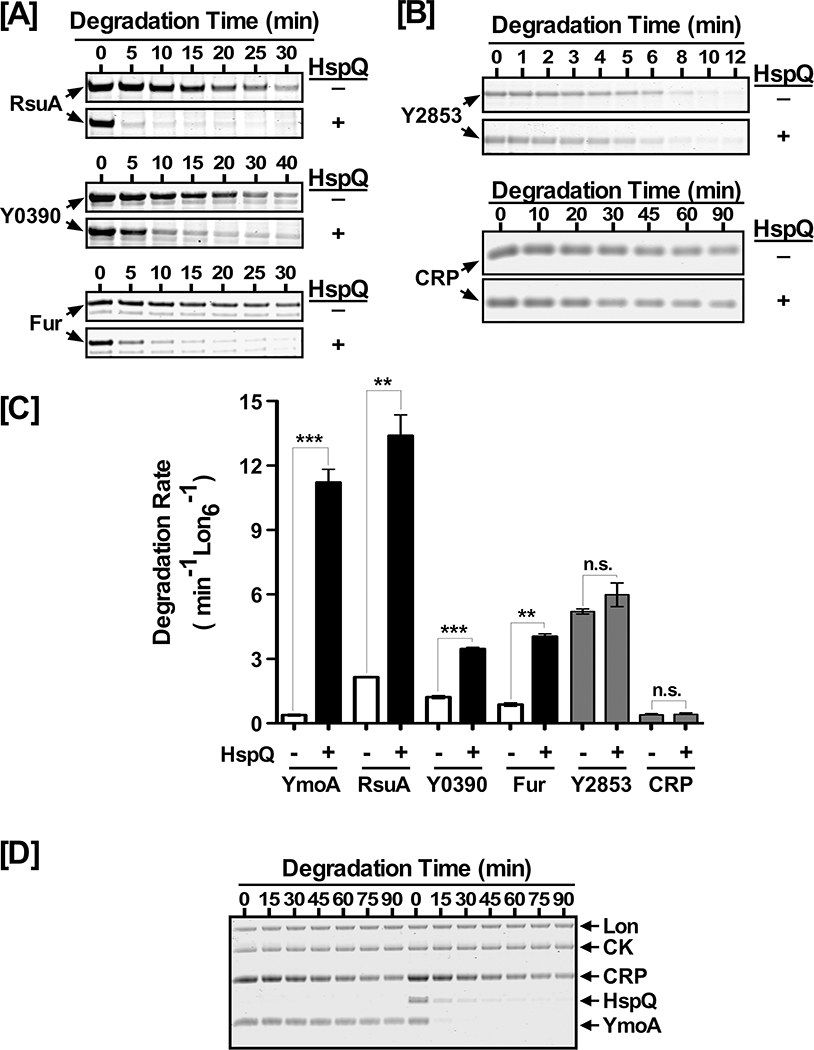
Figure 3: HspQ allosterically activates Lon for enhanced degradation of multiple Lon substrates.
In vitro Lon proteolysis assays were performed for (A) RsuA, Y0390, and Fur and (B) Y2853 and CRP. Each protein was examined at 10 μM concentration in the presence or absence of 10 μM HspQ. Reactions were carried as described in Fig 1D. (C) YmoA, RsuA, Y0390, Fur, Y2853, and CRP degradation rates were calculated in absence and presence of HspQ and plotted to illustrate the HspQ effect on their degradation by Lon. p-values from one-tailed t-test between absence and presence of HspQ for each substrate were calculated as *** p<0.0001 (YmoA), ** p=0.0038 (RsuA), *** p=0.0008 (Y0390), ** p= 0.0041 (Fur), n.s. p= 0.1389 (Y2853), n.s. p= 0.1124 (CRP). (D) HspQ specifically enhances YmoA degradation by Lon in the presence of an additional substrate, CRP. In vitro proteolysis reactions for YmoA and CRP in absence and presence of HspQ were carried out under conditions specified in (A). Representative Coomassie Brilliant Blue stained gels are shown, and the data presented in graphs are from three independent experiments (mean ± SEM).