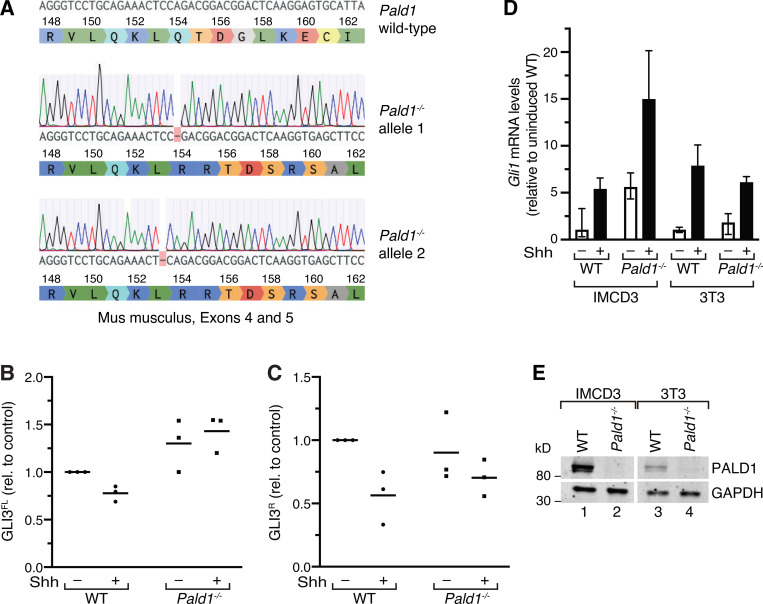
Figure S4.
Full-length GLI3 levels are increased in Pald1−/− IMCD3 cells. (A) cDNA preparation of a CRIPSR/Cas9 genome-edited Pald1−/− IMCD3 cell clone was sequenced and aligned with the PALD1 WT gene sequence from M. musculus. Single-base-pair deletions in exon 4 lead to biallelic frameshift mutations and protein truncation. The DNA sequences have been analyzed using Benchling. (B and C) Quantitation of GLI3 full-length (FL) and repressor (R) forms. Lysates of WT and Pald1−/− IMCD3 cells cultured in the presence or absence of Shh were separated by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by immunoblotting (as in Fig. 8 B). Dot plots show relative GLI3 full-length (GLI3FL; B) and repressor (GLI3R; C) signals normalized to GAPDH, quantified from three independent experiments (n = 3). Horizontal lines indicate means. Each experiment was internally normalized to the relative signals in WT in the absence of signal (WT −Shh ratios = 1). (D) Indicated cell lines were serum-starved for 48 h in the presence or absence of Shh. Gli1 transcript levels were determined using reverse transcription quantitative real-time PCR. Shown are means of relative transcript levels normalized to Gapdh (n = 2). (E) Cell lysates of indicated WT and Pald1−/− cell lines were separated by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by Western blotting using PALD1- and GAPDH-specific antibodies.