Figure 7.
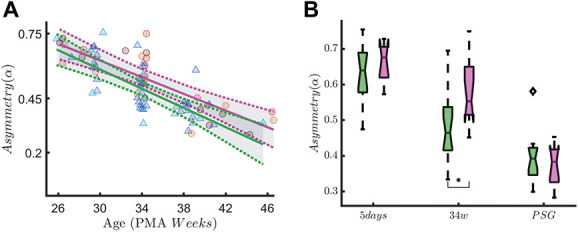
Range EEG asymmetry in early-GA patients. The figure shows the association between the rEEG asymmetry in the alpha band (asymm, Left Panel A) and early skin-breaking procedures (SBPs). Data are reported for the patients with gestational age below 29 weeks during QUIET sleep (QS). The left panel shows how the asymm trend differs in case of high SBPs (magenta curve, SBP ≥50) compared to low SBPs (green curve, SBP <50). Skin-breaking procedures seem to increase the level of asymm throughout the development. The right panel shows the boxplot trend as output of the two-way ANOVA: the division between HIGH SBPs and LOW SBPs is reported for each recording time. A significant SBP-by-measuring point interaction on rEEG asymmetry is found in quiet sleep (F(2,71) = 3.86, P = 0.03). Asymmetry also decreases over time (main effect of measuring point: F(2,71) = 61.61, P ≤ 0.01). At the 34-week recording, infants in the high SBP group showed a significantly higher rEEG asymmetry than the infants in the low SBP group (P = 0.02, indicated as * in the figure). At the recording at 5 days and the PSG recording, this difference did not reach significance (P = 0.91 and P = 0.98, respectively). ANOVA, analysis of variance; GA, gestational age; rEEG, range EEG.
