Figure 6.
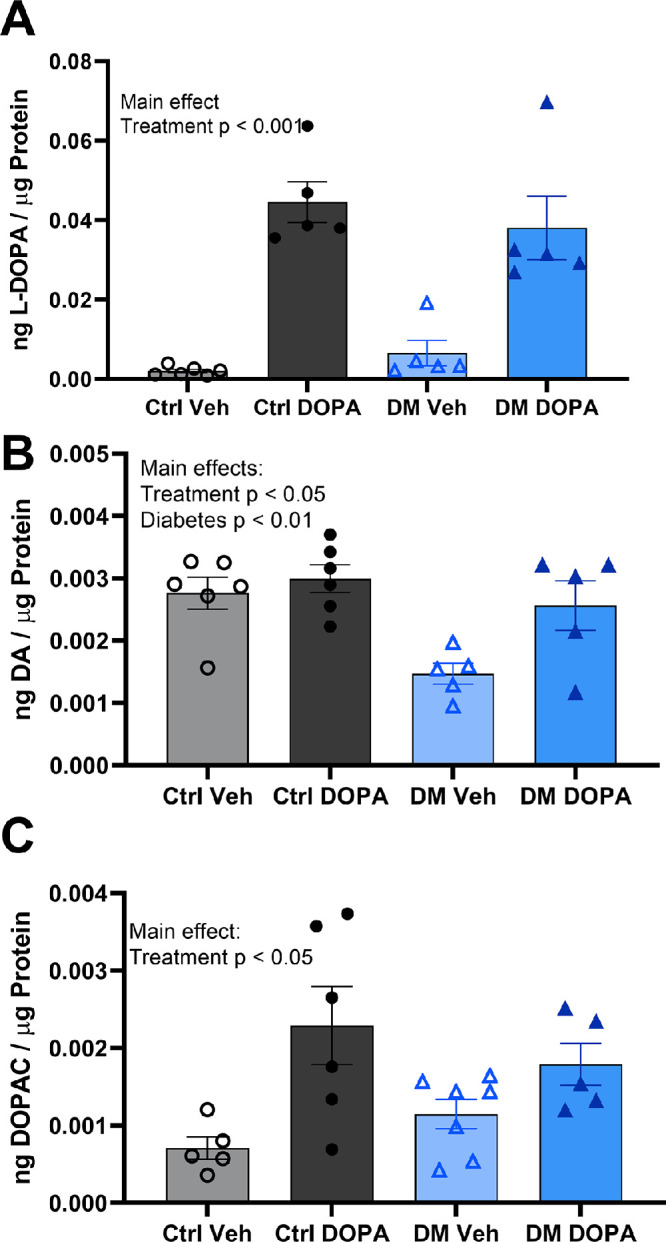
L-DOPA treatment restored reduced retinal dopamine in diabetic rats. L-DOPA treatment significantly increased (A) L-DOPA, (B) dopamine, and (C) DOPAC levels compared with vehicle treated rats, two-way ANOVA, main effects: F (1, 18) = 44.98, P < 0.0001; F (1, 18) = 5.960, P = 0.0252; and F (1, 17) = 19.06, P = 0.0004, respectively. Diabetes significantly decreased (B) dopamine levels in the retina, two-way ANOVA, main effect F (1, 18) = 10.12, P = 0.0052), but not L-DOPA or DOPAC levels. Data plotted as mean ± standard error of the mean.
