Figure 6.
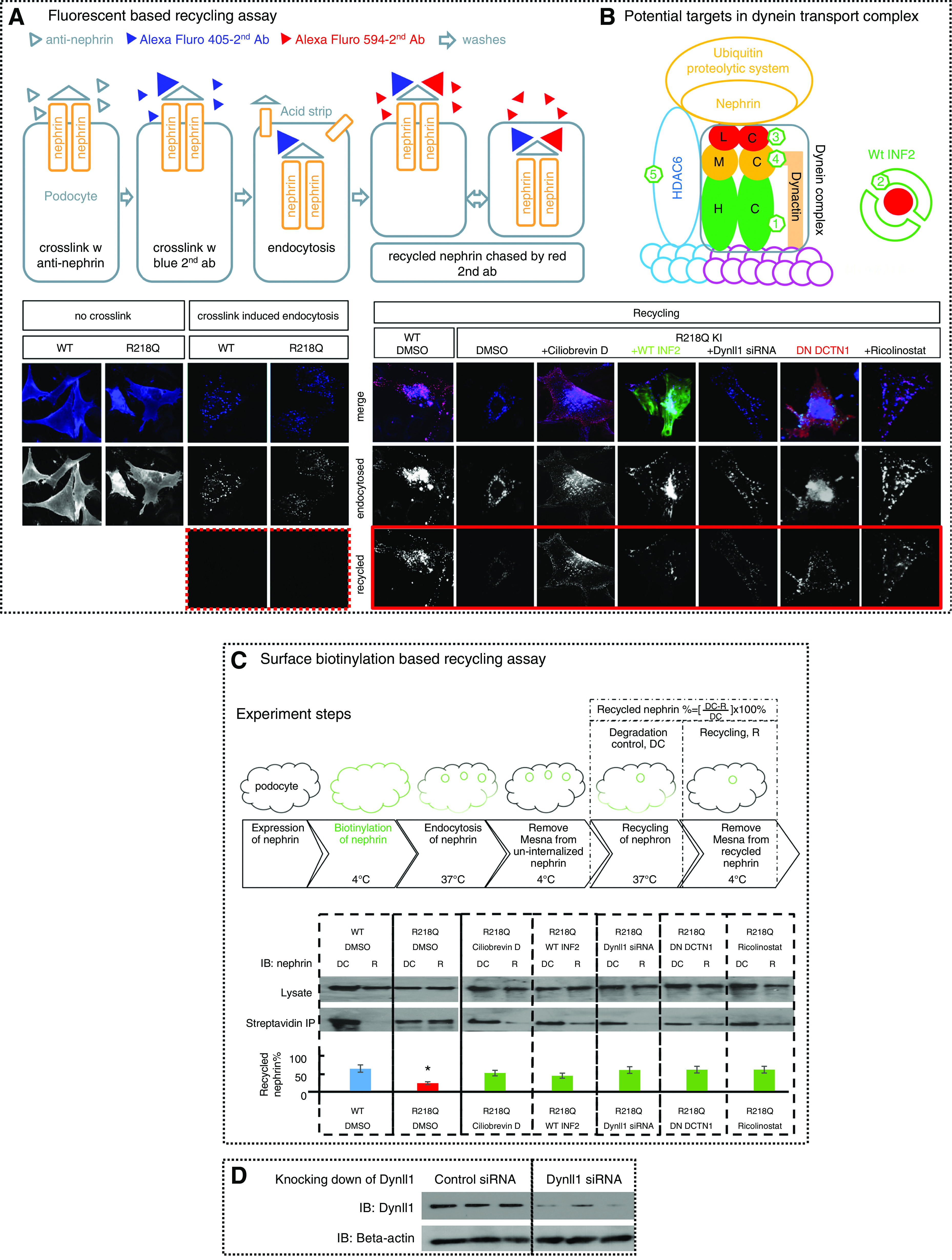
Antagonizing dynein trafficking pathway rescued impaired-nephrin recycling in R218Q KI cells. Nephrin recycling in WT and R218Q KI cells was visualized using (A) a fluorescent-based nephrin recycling assay and (C) quantified by surface biotinylation–based recycling assay. (A) As shown schematically, nephrin expressed on podocytes was crosslinked by anti-nephrin antibody, followed by Alexa Fluor 405–labeled second antibody. After endocytosis and acid strip, cells stained with Alexa Fluor 594–labeled second antibody showed successful removal of uninternalized anti-nephrin (dotted frame). Then the recycled nephrin was chased by Alexa Fluor 594–labeled second antibody (Alexa Fluor 488–labeled second antibody in cells transfected with DesRed DN-DCTN1) (solid frame). (B) A schematic of potential targets in the dynein transport complex. (1) Ciliobrevin D that inhibits the ATPase of the heavy chain (HC); (2) overexpression of GFP-WT INF2-DID that binds to and trap Dynll1; (3) Dynll1 siRNA; (4) dominant negative dynactin 1 (DesRed-DN-DCTN1); and (5) HDAC6 inhibitor (Ricolinostat). (C) Schematics of surface biotinylation–based recycling assay: cells went through a workflow from surface biotinylation of the surface nephrin, endocytosis, and recycling of the biotinylated nephrin, incubation with mesna to strip biotin off the recycled nephrin. Cells collected before (degradation control, DC) and after the mesna strip (recycling, R) were lyzed. The biotinylated nephrin in DC and in R were analyzed by streptavidin IP and normalized to total nephrin. The recycled nephrin is quantitated as biotinylated nephrin ([DC-R]/DC) ×100%. Data were collected from three independent experiments and analyzed using one-way ANOVA, and the differences between groups were analyzed by SNK q test. *P<0.05 versus WT control (DMSO). The impaired nephrin recycling in R218Q KI cells was rescued by coexpression of dominant negative dynactin 1(DN DCTN1), Dynll1 siRNA, WT INF2-DID, Ciliobrevin D (50 μM), or Ricolinostat (5 μM). (D) Knocking down of Dynll1 in R218Q KI cells using Dynll1 siRNA was demonstrated by western blotting, compared with cells treated with control siRNA with no targetable mRNA (sequences of these siRNA duplexes are listed in Methods).
