Figure 2.
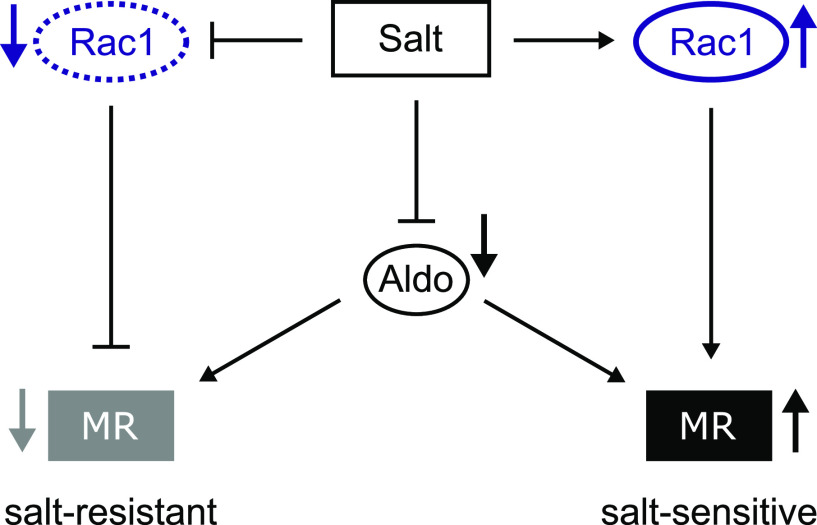
Rac1 is a determinant of BP salt sensitivity through the on/off switching of MR activation. In both salt-resistant and salt-sensitive models, high salt intake suppressed plasma aldosterone (Aldo) concentration. In salt-resistant models, the salt loading suppresses renal Rac1 activity and subsequently, suppresses MR activity to maintain normal BP. In contrast, despite decreased plasma Aldo, high salt activates Rac1 in salt-sensitive models, which causes paradoxical activation of MR, leading to salt-induced BP elevation. The contrasting regulation of MR by Rac1 plays a key role in the development of salt-resistant and salt-sensitive phenotypes in each model.