Figure 2.
Sub-volume averaging of thin filaments reveals the interaction of a double-head myosin with the thin filament and two conformations of light chain domains within a double-head
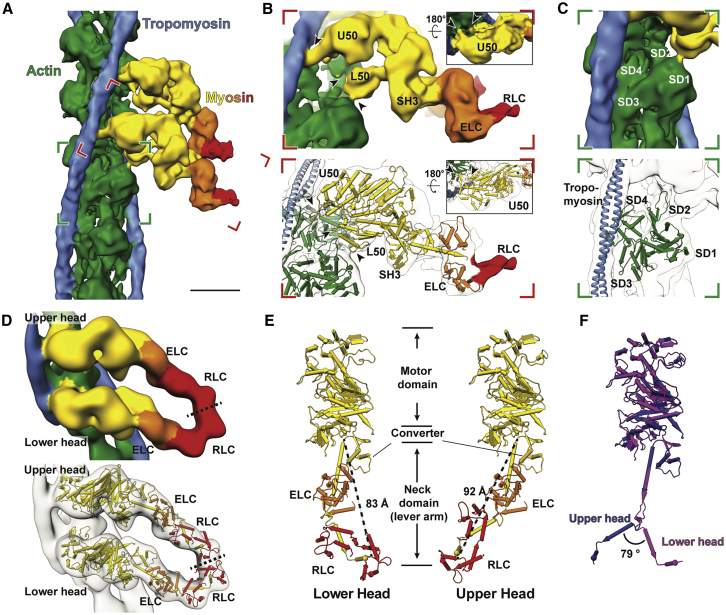
(A) Surface view of the in situ actomyosin structure, showing actin filament (green), tropomyosin (blue), and myosin double heads, with motor domains (yellow), essential light chains (orange), and regulatory light chains (red). Scale bar, 5 nm.
(B) Close-up view of the lower myosin head and homology models based on PDB: 3I5G, 5JLH, and 6KN8. The upper 50 kDa (U50), lower 50 kDa (L50), SH3, and essential light chains (ELC) can be allocated in the map, along with part of the regulatory domain (RLC). Arrow heads indicate the interaction interfaces between actin and myosin at loop 4, helix-loop-helix motif, loop 3 of myosin (top to bottom). Arrow heads in the inset depict interaction interfaces at the cardiomyopathy loop and loop 2 (left to right).
(C) Close-up of an actin subunit and structural model fitted into the EM map showing the four subdomains of an actin subunit (SD1–SD4).
(D) Surface view of the structure of a complete myosin double-head including RLCs determined from averaging shifted sub-volumes (see Figure S4). Their interface is indicated by a dotted line.
(E) Comparison between the lower and upper heads within one double head, showing two different conformations in the lever arm that interacts with RLC and ELC. Lengths of the lever arms were measured between G772 and L844.
(F) Alignment of the lower (purple) and upper (blue) heads heavy chain, showing two different kinks between the ELC-binding region and the RLC-binding region.
See also Figures S2 and S3.