Figure 4: Fatty acid transport genes mediate ven/aza resistance of LSCs.
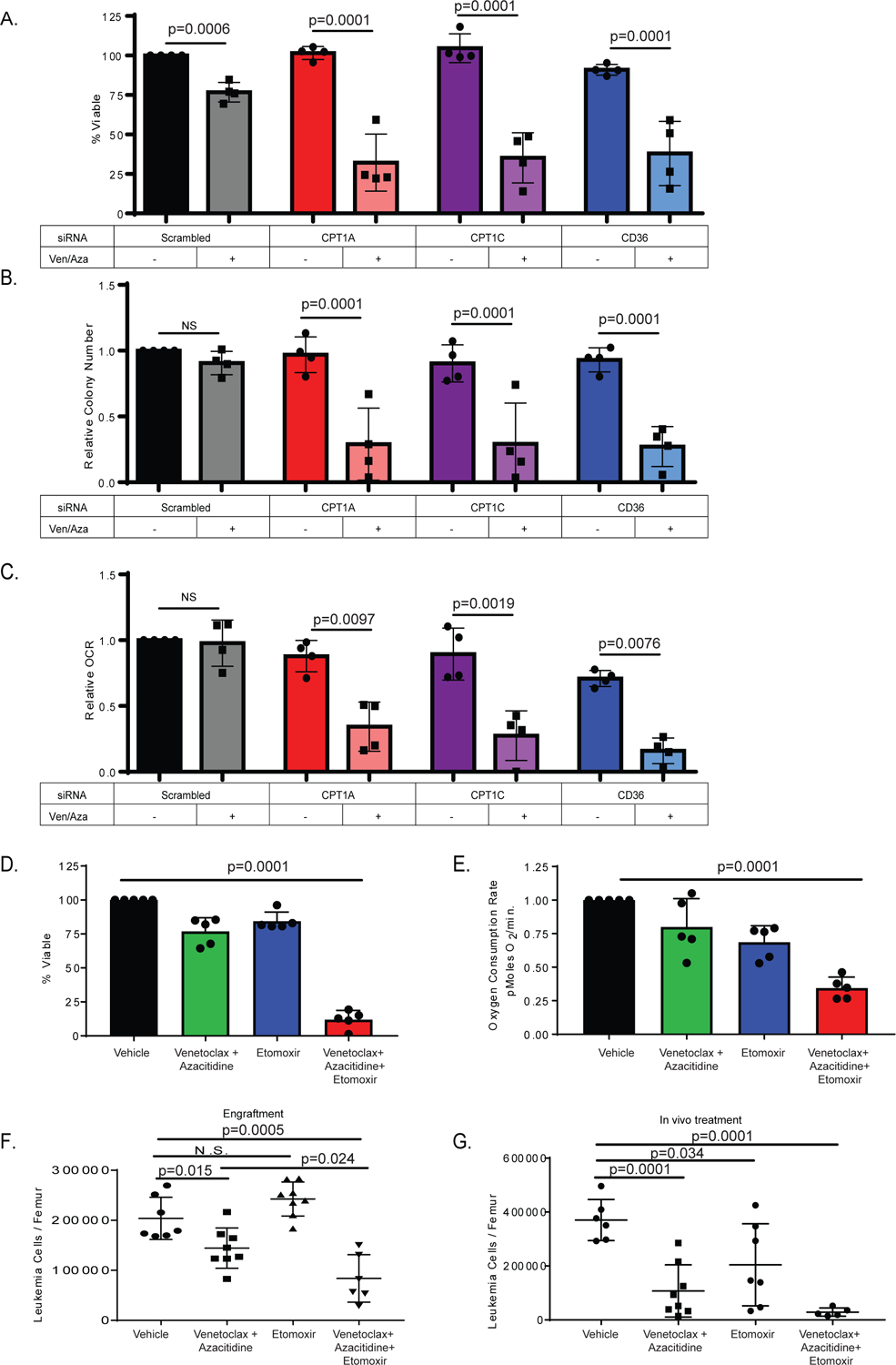
A. siRNA knock-down of Cpt1A, Cpt1C, and CD36 in combination with ven/aza decreases viability of resistant LSCs. N= 4 resistant primary AML specimens (2 RAS pathway mutants). Data are presented as mean values +/− SD. Significance was measured by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test. [B]. colony-formation assays and [C] oxygen consumption rates for the same specimens and conditions shown in panel. Data are presented as mean values +/− SD. Significance was determined using 2-way Anova analysis. D. Etomoxir in combination with ven/aza decreases viability of resistant LSCs. N= 5 resistant specimens (1 RAS pathway mutant). Data are presented as mean values +/− SD. Significance was measured by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-. E. Etomoxir in combination with ven/aza decreases OCR of resistant LSCs. N= 5 resistant specimens (1 RAS pathway mutant). Data are presented as mean values +/− SD. Significance was measured by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test. F. A ven/aza resistant LSC specimen was treated ex vivo for 24 hours with the indicated conditions and transplanted into immune deficient NSG-S mice. Cells were dosed with 50 uM Etomoxir, 500 nM Venetoclax, and 2.5 uM Azacitidine in the combinations indicated. At 6 weeks post-transplant, the levels of human leukemia cells in the bone marrow was determined (N = 7 mice in vehicle group, N = 8 mice in the venetoclax with azacitidine group, N = 8 mice in the etomoxir group, and N = 6 in the venetoclax + azacitidine + etomoxir group. Data are presented as mean values +/− SD. Significance was measured by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test. G. In vivo treatment with etomoxir in combination with ven/aza significantly decreased tumor burden in patient derived xenograft. (N = 6 mice in vehicle group, N = 8 mice in the venetoclax with azacitidine group, N = 7 mice in the etomoxir group, and N = 5 in the venetoclax + azacitidine + etomoxir group. Data are presented as mean values +/− SD. Significance was measured by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test.
