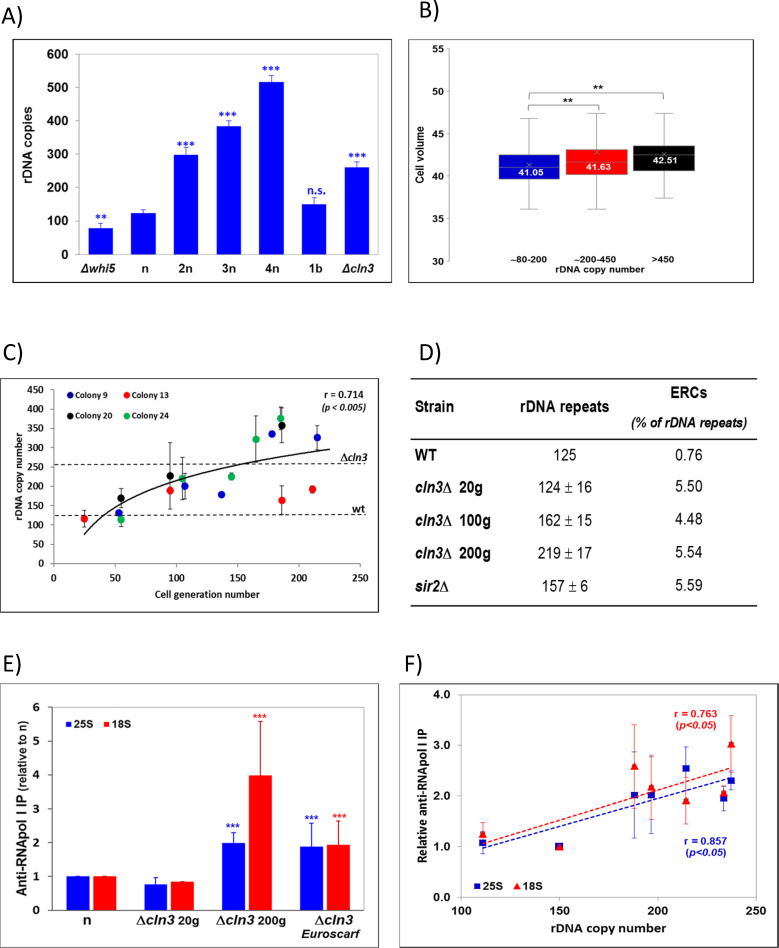
Fig 2. The number of rDNA repeats evolves in a cln3 mutant to match the optimum value of the RNA pol I nTR required for its cell volume.
A) The number of rDNA repeats varies in different strains in such a way that it depends on ploidy, except for cell size haploid mutants (see S1C Fig). A t-test was used for statistical significance: n.s (not significant), ***: p-value < 0.0005; **: p-value < 0.005. B) The average cell volume for the mutant strains from the Kobayashi database [29] was calculated for the three groups of “normal” rDNA repeat copy number (#80–200), high copy number (#299–400) and very high copy number (>450) using the cell volume data (in fL) from [21]. A similar plot, but using the cell volume data (in arbitrary units) from [32], is shown in S1B Fig. The difference was maintained even with the mutants with a very low growth rate (using the data from [32]). We filtered out mutants at the 1.3-, 1.5- or 1.7-fold lower growth rates than the wild type. The values obtained for average cell volumes were exactly the same as those shown in panel B. C) In an “early” cln3 mutant, the copy number is small, similar to its parental wt haploid (n: BY4741) when it is a recent transformant, but increases along with the number of generations for four independent clones (#9,13,20,24). The dashed horizontal lines mark the repeat copy number for strains Euroscarf Δcln3 (BQS2006) and wt (BY4741). D) Extrachromosomal rDNA circles (ERCs) analysis. The DNA from different strains was isolated and quantified, electrophoresed, blotted and hybridized with ACT1 and 18S rDNA probes. See S2 Fig for an example of electrophoresis. The number of repeats corresponded to the 18S/ACT1 ratio and relativized to the wild type (125 copies). The percentage of ERCs corresponded to the ratio of all the ERCs bands (see S2 Fig) to the genomic DNA band. Two repeats of the experiment were done. The values represent the averages and standard deviations (SD) for them. The wild-type sample (BY4741) had no SD because it was taken as an internal reference of intensity in each replicate using the calculated copy number of 125 repeats (panel A). E) The RNA pol I nTR of the different cln3 mutants varies according to the rDNA repeat number, as determined by the chromatin immunoprecipitation of the second largest RNA pol I subunit (A135) onto either the 25S (blue) or 18S (red) transcribed regions. Strain Δcln3 Euroscarf is BQS2006 (see S1 Table). A t-test was used for statistical significance of the differences between the freshly obtained (20 generations, 20g) Δcln3 mutant and the evolved Δcln3 (“late” 200g and Euroscarf) mutants: ***: p-value < 0.0005. F) The RNA pol I nTR of the Δcln3 mutants increase in parallel to the rDNA repeat number during the evolution experiment. The nTR was calculated as in E).