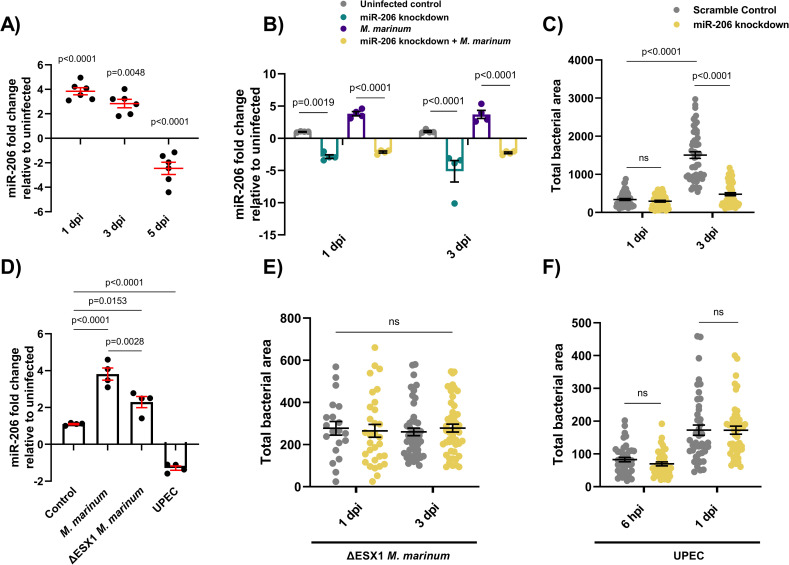
Fig 1. Infection-induced miR-206 expression alters bacterial burden.
(A) Expression of miR-206 analysed by qPCR at 1, 3, and 5 dpi. (B) Expression of miR-206 in uninfected and infected antagomir-injected embryos (miR-206 knockdown). (C) M. marinum burden in miR-206 knockdown embryos at 1 and 3 dpi. (D) Expression of miR-206 at 1 dpi following infection with either wild-type (WT) M. marinum, ΔESX1 M. marinum, or UPEC. (E) ΔESX1 M. marinum burden in miR-206 knockdown embryos at 1 and 3 dpi. (F) UPEC burden in antagomir-injected embryos at 6 hpi and 1 dpi. Each data point represents a single measurement, with the mean and SEM shown. For qPCR analysis, each data point represents 10 embryos, and contains 2 biological replicates. Bacterial burden analysis data points (WT M. marinum, ΔESX1 M. marinum, and UPEC) represent individual embryos (n = 40–50 embryos per group) and are representative of 2 biological replicates.