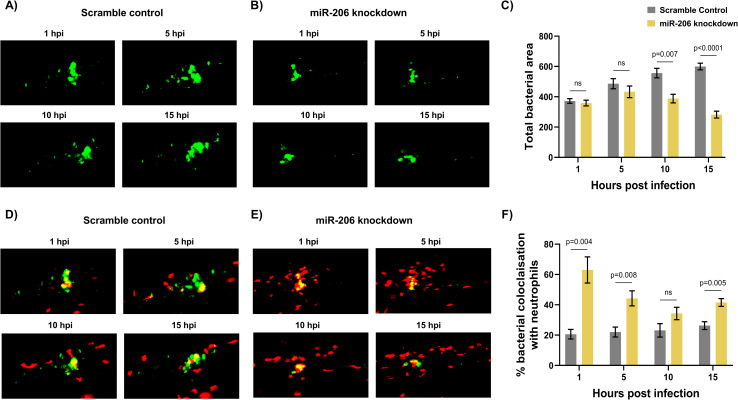
Fig 4. Increased miR-206 knockdown-associated neutrophils prevent bacterial dissemination.
(A-B) Representative images of bacterial granulomas in trunk-infected control and miR-206 knockdown embryos. (C) Quantification of M. marinum burden in trunk-infected control and miR-206 knockdown embryos. (D-E) Representative images of M. marinum-neutrophil interactions in trunk-infected control and miR-206 knockdown embryos. Neutrophils are red Tg(lyzC:dsred) and M. marinum is green (wasabi); co-localisation is indicated by yellow fluorescence. (F) Quantification of the proportion of the bacterial fluorescence overlapping with neutrophil fluorescence (co-localisation yellow fluorescence in D-E) in trunk-infected control and miR-206 knockdown embryos. Each data point represents the mean of 6 foci of infection from 6 separate embryos with SEM shown. Differences between groups was calculated using multiple t-tests and the Holm-Sidak method.