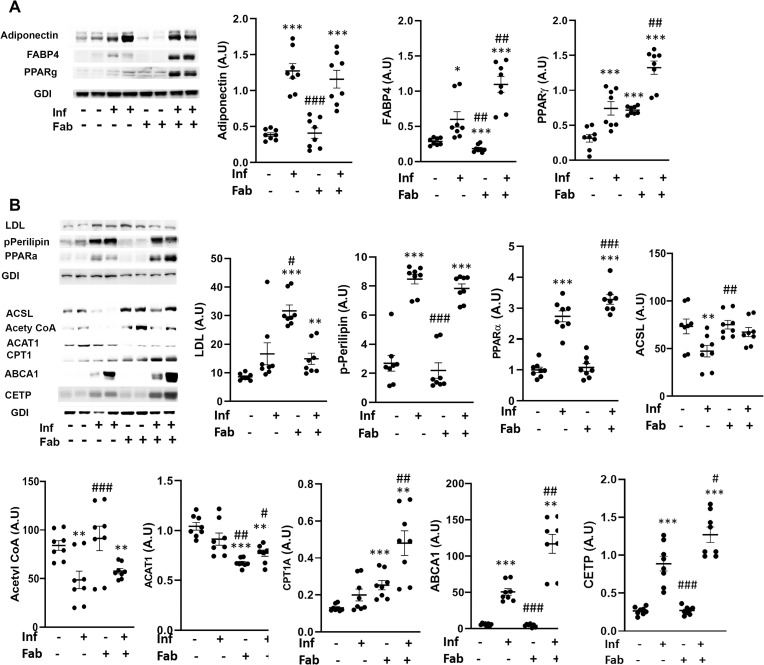
Fig 6. Fat ablation increases adipogenic signaling and elevates lipid levels in the hearts during the early chronic stage in T. cruzi infected mice.
Immunoblot analysis of (A) adipogenic markers (FABP4, PPARᵧ and adiponectin), and (B) lipid metabolism (LDL and lipid metabolism markers (p-perilipin, PPARα, acyl-CoA ligase (ACSL) and acetyl Co-A carboxylase, CPT1, ABCA1 and CETP) in the hearts of indicated mice (infected or uninfected mice, fat-ablated (Fab +) or fat-unablated (Fab -) n = 8). The change in protein levels were normalized to the levels of Guanosine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor (GDI) and plotted column scatter graph. The error bars represent SEM. A.U. indicates arbitrary unit. *p≤0.05, **p≤0.01 or ***p≤0.001 compared with uninfected fat-unablated. #p≤0.05, ##p≤0.01 or ###p≤0.001 compared with infected fat-unablated.