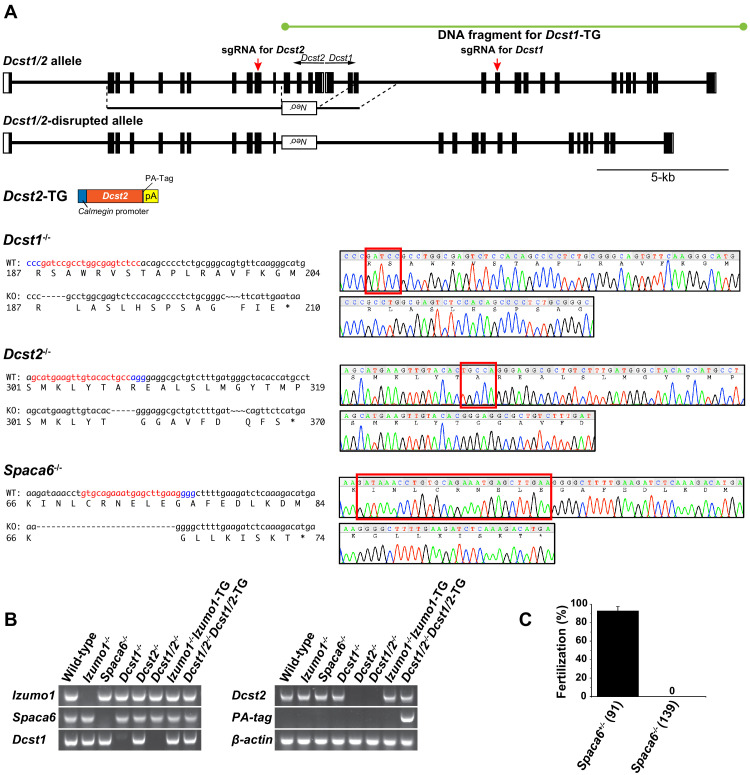
Figure 2. Strategy for Dcst1 and Dcst2 genes disruption and its validation.
(A) Targeted disruption of the Dcst1/2, Dcst1, Dcst2, and Spaca6 genes, and constructs for Dcst1 and Dcst2 transgenic mice. Complete structures of the wild-type mouse Dcst1/2 alleles are shown. Exons and introns are represented by boxes and horizontal lines, respectively. An open reading frame for Dcst1 and Dcst2 genes is shown in black. For the targeted disruption of mouse Dcst1/2, the neomycin-resistance gene (Neor) was inserted between Dcst1 exon 3 and Dcst2 exon 4. A herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene was introduced into the targeting construct for negative selection. For the gene complementation experiments, transgenic mouse lines expressing dendrocyte expressed seven transmembrane protein domain-containing 1 (DCST1), in which full-length genome DNA fragment including all promoter region, exons, and introns was incorporated, and dendrocyte expressed seven transmembrane protein domain-containing 2 (DCST2), in which full-length cDNA with a PA-tag sequence was inserted between a testis-specific (pachytene spermatocyte to spermatid stage) Calmegin promoter and rabbit β-globin polyadenylation signal, were produced. For genome-editing of Dcst1, Dcst2, and Spaca6 using the CRISPR/Cas9 system, the red and blue letters show the target and protospacer adjacent motif (PAM) sequence, respectively (left panels). A DNA sequence chromatogram shows that Dcst1-/-, Dcst2-/-, and Spaca6-/- had 5-base, 5-base, and 28-base deletions, respectively. The deleted sequences are boxed in red (right panels). (B) Validation of gene disruption by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). All primer sets employed wild-type mRNA-specific oligonucleotide sequences except for PA-tag. As a result, all gene disruptions and transgenes were confirmed appropriately. β-actin mRNA was used as an internal control. (C) In vitro fertilization analysis using Spaca6+/- and Spaca6-/- spermatozoa (n = 4 and 4, respectively). The fertilization rate was evaluated at the two-cell stage embryo. The numbers in parentheses indicate the numbers of oocytes used. The error bars represent standard error of the mean (s.e.m.).