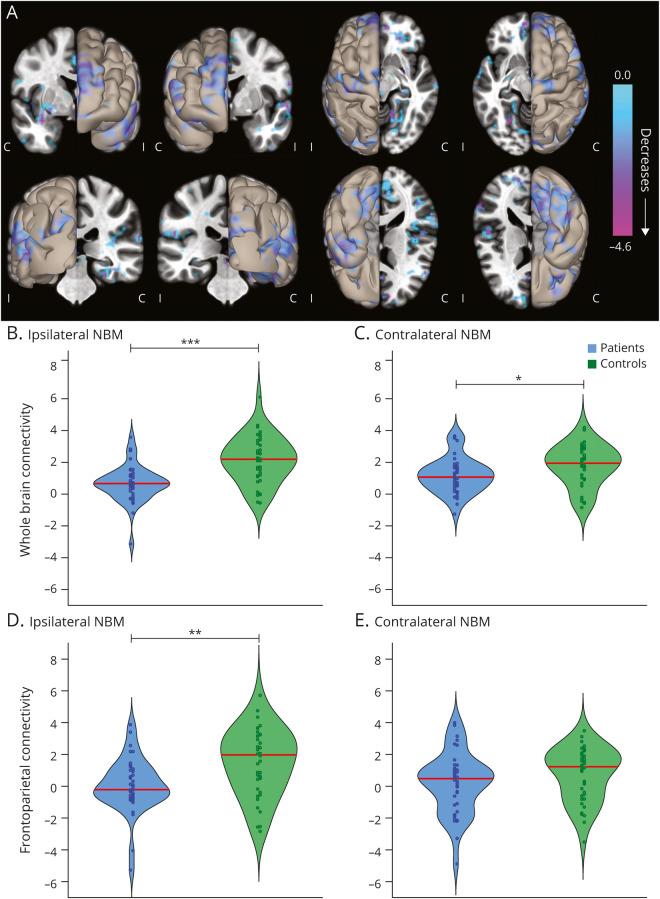
Figure 1. Functional Connectivity of the NBM Is Decreased in Patients With TLE Compared to Controls.
(A) Data represent seed-to-voxel fMRI functional connectivity maps (bivariate correlation) seeded from bilateral nucleus basalis of Meynert (NBM), comparing patients with temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE) vs control participants (paired t test, cluster threshold level p < 0.05, false discovery rate correction). These seed-to-voxel group-level comparisons are projected onto an average brain template. Negative contrasts are shown, and no connectivity increases were seen in patients. fMRIs are oriented with respect to the side of seizure onset for patients with TLE, and matched controls images are flipped accordingly. In evaluating functional connections between NBM and all other regions in the brain (excluding cerebellum), NBM connectivity reductions in patients with TLE vs controls are observed both (B) ipsilateral and (C) contralateral to the side of seizure onset. Restricting the analysis to selected frontoparietal regions, large reductions in NBM connectivity are noted in patients vs controls on the (D) ipsilateral but not (E) contralateral side. Red line shows median. N = 40 patients with TLE and 40 matched healthy control participants. C = contralateral; I = ipsilateral. ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05, paired t tests with Bonferroni-Holm correction.