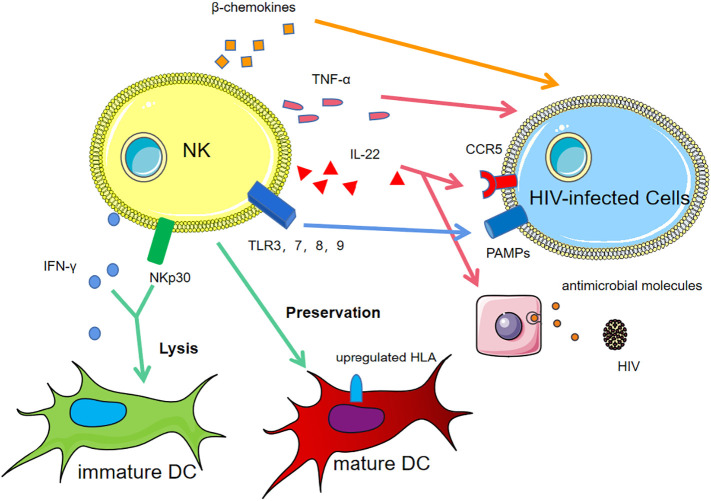
Fig. 2.
The anti-HIV mechanisms of NK cells.
In human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected individuals, the natural killer(NK) cells /dendritic cells (DCs) interaction lyses immature DCs via NKp30 and IFN-γ and preserve mature DCs via upregulating HLA molecules, called “DC editing”. Toll-like receptor (TLR)3, TLR7, TLR8 and TLR9 on NK cells recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) on infected cells, activating NK cells. NK cells produce increased tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-α and the β chemokines.
Uninfected individuals produce high levels of IL-22, downregulating chemokine receptor 5 (CCR5) expression and inducing epithelial cells to produce antimicrobial molecules.