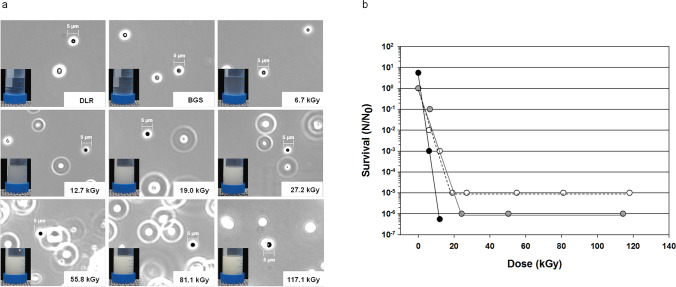
Fig. 3.
a Anoxic exposure of I. hospitalis stationary phase cultures to gamma radiation, and transfer into Falcon® tubes after irradiation. I. hospitalis cells can be seen as black cocci (scale bar = 5 µm), whereas strong refractive particles are ascribed to elemental sulfur. The numbers in the lower right corner represent the applied dose in kGy. DLR represents the laboratory control, whereas BGS stands for the transport control. b Influence of γ-ray-exposed, sulfur-containing and sulfur-free ½ SME medium on the survival of I. hospitalis in comparison to serial diluted γ-ray-exposed I. hospitalis cells. Black circles: serial dilution of I. hospitalis stationary phase cells prior to exposure. The diluted samples were exposed to ionizing radiation, and directly incubated afterwards. Open circles: serial dilution of untreated I. hospitalis cells in γ-ray-exposed ½ SME + S0 medium. Gray circles: serial dilution of untreated I. hospitalis cells in γ-ray-exposed ½ SME-S0 medium supplemented with unexposed S0 after exposure. The experiments were conducted with n = 1 and the trendlines fitted by hand (Koschnitzki 2016)