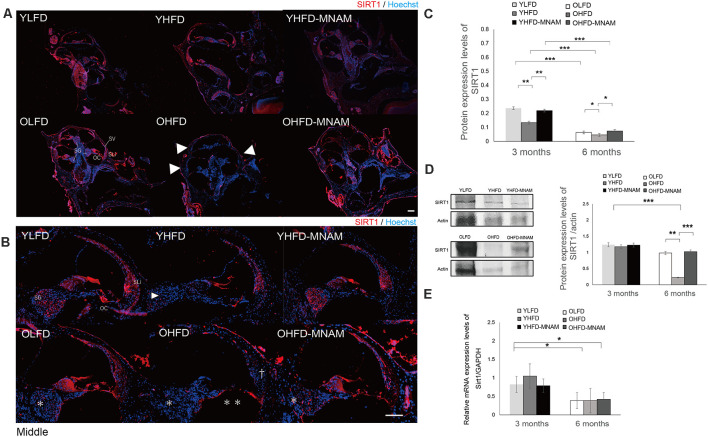
Figure 5.
SIRT1 expression in the cochlea: the age-related SIRT1 downregulation of expression observed in OHFD mice is absent in OHFD-MNAM mice. (A) SIRT1 staining (red) of the whole cochlea at 3 and 6 months after commencement of the experiment. SIRT1 is prominently localized in the OCs, SGCs, and type II and IV SLi cells in all turns within the cochlea. The arrowheads indicate a decrease in SIRT1 expression in the cochlea of the OHFD mice. (B) SIRT1 staining (red) of the middle turn of the cochlea at 3 and 6 months after commencement of the experiment. The arrowhead indicates a decrease in SIRT1 expression in the SGCs in the cochlea of the YHFD mice after experiment initiation. The asterisks indicate a decrease in SIRT1 expression in the SGCs in the cochlea of the OHFD mice after experiment initiation. The double asterisk indicates a decrease in SIRT1 expression in the OCs in the cochlea of the OHFD mice after experiment initiation. The dagger symbol indicates a decrease in SIRT1 expression in the SLi in the cochlea of the OHFD mice after experiment initiation. (C) The SIRT1 protein expression in the cochlea quantitatively analyzed using ELISA at 3 and 6 months after commencement of the experiment. The SIRT1 protein expression analyzed via ELISA decreased with aging (p < 0.001 in each group). The YHFD and OHFD groups exhibited a decrease in the SIRT1 protein expression compared with the YLFD and OLFD groups (p = 0.002 and p = 0.04). In the YHFD-MNAM and OHFD-MNAM, decrease in the SIRT1 protein expression was lower than that in the YHFD and OHFD groups (p = 0.004 and p = 0.01; All groups, n = 5; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001). (D) The SIRT1 protein expression in the cochlea quantitatively analyzed using WB analysis at 3 and 6 months after commencement of the experiment. β-actin expression was used as a reference. The OHFD mice exhibited a greater decrease in the SIRT1 protein expression compared to the OLFD mice (p = 0.001). In the OHFD-MNAM group, decrease in the SIRT1 protein expression was less than that in the OHFD group (p < 0.001; All groups, n = 5; **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001). (E) Sirt1 mRNA expression in the cochlea quantitatively analyzed using qRT-PCR at 3 and 6 months after commencement of the experiment. GAPDH expression was used as a reference. Sirt1 mRNA expression analyzed via ELISA decreased with aging (p = 0.03 in the YLFD and OLFD, p = 0.02 in the YHFD and OHFD, p = 0.04 in the YHFD-MNAM and OHFD-MNAM). The YHFD and OHFD mice did not exhibit a decrease in Sirt1 mRNA expression compared with the YLFD and OLFD groups (p = 0.14 and p = 0.49). In the YHFD-MNAM and OHFD-MNAM groups, there were no decreases in Sirt1 mRNA expression compared with those in the YHFD and OHFD groups (p = 0.11 and p = 0.45; Bars: 100 μm; Sirt1, Sirtuin 1; YLFD, low-fat diet-fed 3-month-old mice; OLFD, low-fat diet-fed 6-month-old mice; YHFD, high-fat diet-fed 3-month-old mice; OHFD, high-fat diet-fed 6-month-old mice; YHFD-MNAM, high-fat diet plus 1% N1-methylnicotinamide-fed 3-month-old mice; OHFD-MNAM, high-fat diet plus 1% N1-methylnicotinamide-fed 6-month-old mice; OCs, the organ of Corti; SGCs, spiral ganglion cells; SLi, spiral ligament; SV, stria vascularis; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; WB, western blotting; mRNA, messenger ribose nucleic acid; qRT-PCR, quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction).