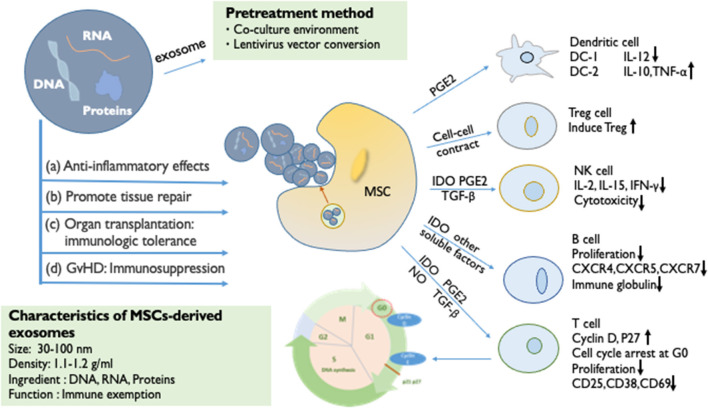
Figure 1.
The immunosuppressive effect of MSCs and MSC-derived exosomes. The immunomodulatory effects of MSCs can be largely attributed to paracrine factors (IDO, PGE2, NO, TGF-β, and exosome). By secreting soluble factors, the proliferation of T cells is inhibited (cell cycle arrest at G0), B cell activation is prevented (reduced proliferative capacity), NK cells are influenced (reduced cytotoxicity), and the differentiation and maturation of DC is affected. Through cell-to-cell contact, it can Tregs can be induced. MSC-derived exosomes are small vesicles of 30–100 nm in diameter, which are rich in important biomolecules such as DNA, RNA, and proteins. MSC-derived exosomes have the same immunosuppressive effect as MSCs. (a) Anti-inflammatory effects. (b) Promotion of tissue repair. (c) Organ transplantation: immunologic tolerance. (d) Immunosuppression in GvHD. The targeted pretreatment of exosomes is an important means of current biological treatment. The method of changing the co-culture environment, and the lentiviral vector transferring functional proteins or mRNA into exosomes, can pre-enhance the activity of exosomes to enhance efficacy.