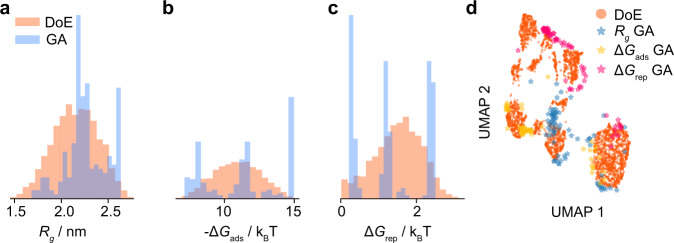
Fig. 8. Distribution of properties for the polymers found by inverting the machine learning models using a genetic algorithm (GA).
To generate new feature vectors, we ran the genetic algorithm with different weights for the novelty part of the loss function—ranging from no penalty for similar polymers to high (50 times the objective) penalty for polymers similar to the ones already sampled with our design of experiments (DoE). In addition, we run the genetic algorithm for different elitist ratios. For each feature vector, three possible polymer bead sequences were generated, as a feature vector does not map to one unique arrangement of monomers. a Distribution of radius of gyration (Rg). b Distribution of adsorption energies ΔGads. c Distribution of dimer repulsion energies ΔGrep. d Polymer properties obtained from GA are projected onto the first two uniform manifold approximation and projection (UMAP) components and are compared to those obtained from DoE. See Supplementary Fig. 30 for principal component analysis.