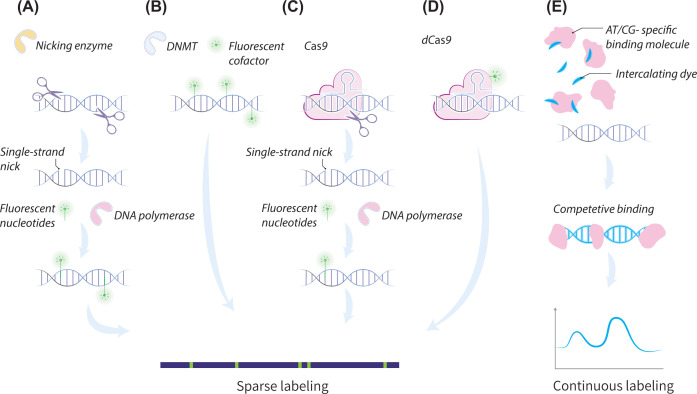
Figure 2. Genetic labeling schemes.
(A–D) sparse labeling schemes. (A) Two-step nick translation. In the first step, a nicking enzyme creates a single-strand nick in the DNA. In the second step, DNA polymerase introduces fluorescent nucleotides to the nicked site. (B) Methyltransferase-based one-step labeling. (C) Nick translation at target sequences with nicking Cas9, steps are similar to (A). (D) single-step fluorescent labeling with dCas9. (E) Continuous affinity-based labeling: competitive binding of a nonsequence-specific fluorescent intercalating dye and an AT/CG-selective molecule. This molecule blocks the dye from binding to these sites, thus keeping them dark while the rest of the genome is labeled, resulting in a sequence-specific intensity profile of the molecules.