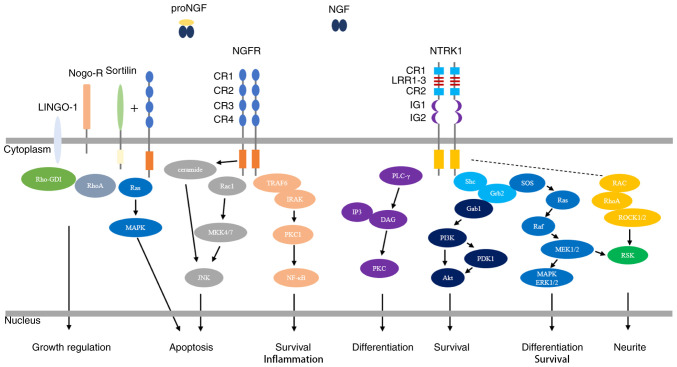
Figure 1.
NGF-mediated regulation of the NGFR and NTRK1 signaling pathways. NGF binds to the extracellular domain of NTRK1 with high affinity, resulting in dimerization of NTRK1 and activation of its intracellular kinase. NTRK1 signaling is best characterized by activation of the three main downstream signal transduction pathways, the MAPK/ERK, PI3K/Akt and PLC-γ signaling pathways, which results in the differentiation and survival of neurites. NGF binds to NGFR with low affinity. NGFR activation involves different molecular mechanisms in different types of cells and tissue environments, and exerts effects via the NF-κB, JNK and ceramide signaling pathways, resulting in apoptosis, survival and inflammation. Interactions of NGFR with sortilin allow the high-affinity binding of proNGF. Subsequent activation of the Ras/MAPK pathway results in apoptosis. Interactions of NGFR with Nogo-R and LINGO-1 play roles in the regulation of growth. Activation of RhoA by the displacement of Rho-GDI inhibits neurite outgrowth from postnatal sensory neurons and cerebellar neurons. NGF, nerve growth factor; NTRK1, tropomyosin-related kinase receptor 1; MAPK/ERK, mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase; PI3K/Akt, phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/serine protein kinase; PLC-γ, phospholipase C-γ; NF-κB, nuclear transcription factor-kappa B; JNK, Jun N-terminal kinase; CR, cysteine-rich; Nogo-R, Nogo receptor; LINGO-1, leucine-rich repeat and immunoglobulin-like domain-containing protein-1.