Figure 1.
Indirect effects of viruses on the apoptotic pathway through deregulation of cellular miRNAs
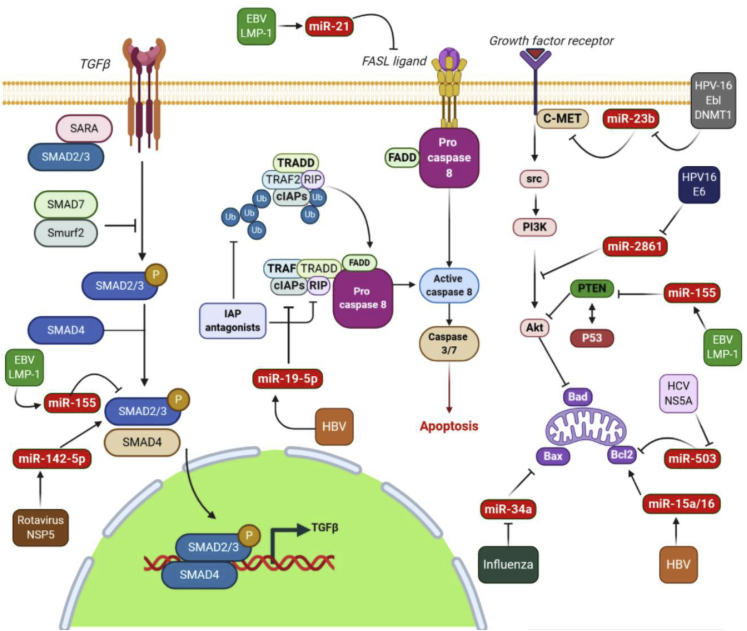
miR-2861 increased the apoptosis of cervical cancer cells through the PI3K/AKT pathway by targeting EGFR. HPV16 E6 is able to downregulate the miR-2861 expression level and can contribute to tumor development. Moreover, HPV-16 E6/DNMT1 can suppress miR-23b expression and contribute to apoptosis resistance through the blocking inhibitory effect of miR-23b on c-MET. EBV-LMP-1 protects B cell lymphoma from rituximab-induced apoptosis via miR-155-mediated Akt activation and upregulation of Mcl-1. LMP1 can increase miR-21 to promote the resistance of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells to cisplatin-induced apoptosis by suppressing PDCD4 and Fas-L. HBV infection can also lead to the induction of apoptosis via the upregulation of miR-194-5p expression in vitro. miR-194-5p-mediated suppression of cFLIP expression strongly sensitizes HepG2 cells to undergo apoptosis in response to a physiological stimulus. The transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) signaling pathway, a major intercellular signaling pathway in mammalian cells, plays a key role in regulating many cellular processes, such as cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. TGF-β signaling is known to depend on the formation of Smad2/3-Smad4 transcription regulatory complexes. EBV LMP-2A inhibits the expression level of Smad2 through regulating miR-155-5p in gastric cancer cell lines and inhibits apoptosis. Rotavirus infection leads to up-regulation of TGF-β, which may lead to early apoptosis thus preventing virus progression. However, rotavirus counteracts this by upregulation of miR-142-5p. Rotavirus NSP5 upregulates miR-142-5p, which targets several components of the TGF-β signaling pathway. The mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis is dependent on the BCL-2 (B cell CLL/lymphoma 2) family of proteins for the efficient release of pro-apoptotic factors from the mitochondrial intermembrane space. The BCL-2 family is divided into three groups based on their primary function: (1) anti-apoptotic proteins (BCL-2, BCL-XL, BCL-W, MCL-1, BFL-1/A1); (2) pro-apoptotic pore formers (BAX, BAK, BOK); and (3) pro-apoptotic BH3-only proteins (e.g., BAD, BID, BIK, BIM). miR-503 and miR-15a/16 can target the 3′ UTR of Bcl-2 and inhibit hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth. However, HCV NS5A and HBV mRNA decrease miR-503 and miR-15a/16 expression, respectively, and increase Bcl-2 expression, which leads to a decrease in apoptosis.