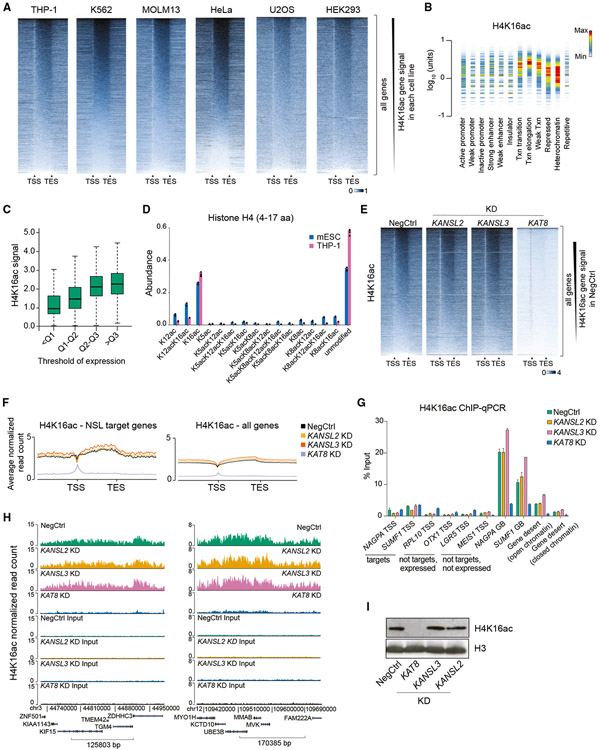
Figure 3. Depletion of KAT8 but not KANSL2 and KANSL3 abrogates global H4K16ac levels.
(A) Heatmaps of H4K16ac ChIP-seq signal at all genes in six human cell lines (gene length is normalized). The signal is normalized to the total number of reads. TSS, transcription start site; TES, transcription end site.
(B) Density plot of normalized THP-1 H4K16ac ChIP-seq signal across different chromatin states defined by the Broad Institute ChromHMM project in K562 cells. Similar results were obtained using K562 H4K16ac ChIP-seq data. Txn, transcription. Color in the density plot conveys shape of the signal distribution normalized to maximum within one lane. The amount of H4K16ac is shown on the y axis.
(C) Boxplots demonstrating statistical summary of H4K16ac ChIP-seq signal in gene bodies of genes binned according to quantile (Q) distribution of expression in THP-1 cells. All groups are significantly different (p < 2.2e-16, two-sided Wilcoxon rank-sum test).
(D) Bar plot indicating abundances of individual H4 peptides (amino acids 4–17) with different acetylation combinations in mouse ESCs and human THP-1 cells measured using mass spectrometry.
(E) Heatmaps of H4K16ac ChIP-seq signal at all genes in NSL complex KD series. The signal is normalized to the number of Drosophila reads (see STAR methods).
(F) Average normalized H4K16ac ChIP-seq profiles across NSL target genes or all genes in NSL complex KD series.
(G) qRT-PCR quantitation of H4K16ac ChIP signal at selected loci after KDs of KANSL2, KANSL3, or KAT8. TSS, transcription start site; GB, gene body. Values are shown as mean ± SD.
(H) Example H4K16ac ChIP-seq tracks in NSL complex KD series.
(I) Western blotting analysis of H4K16ac and H3 levels after KANSL2, KANSL3, or KAT8 KDs.