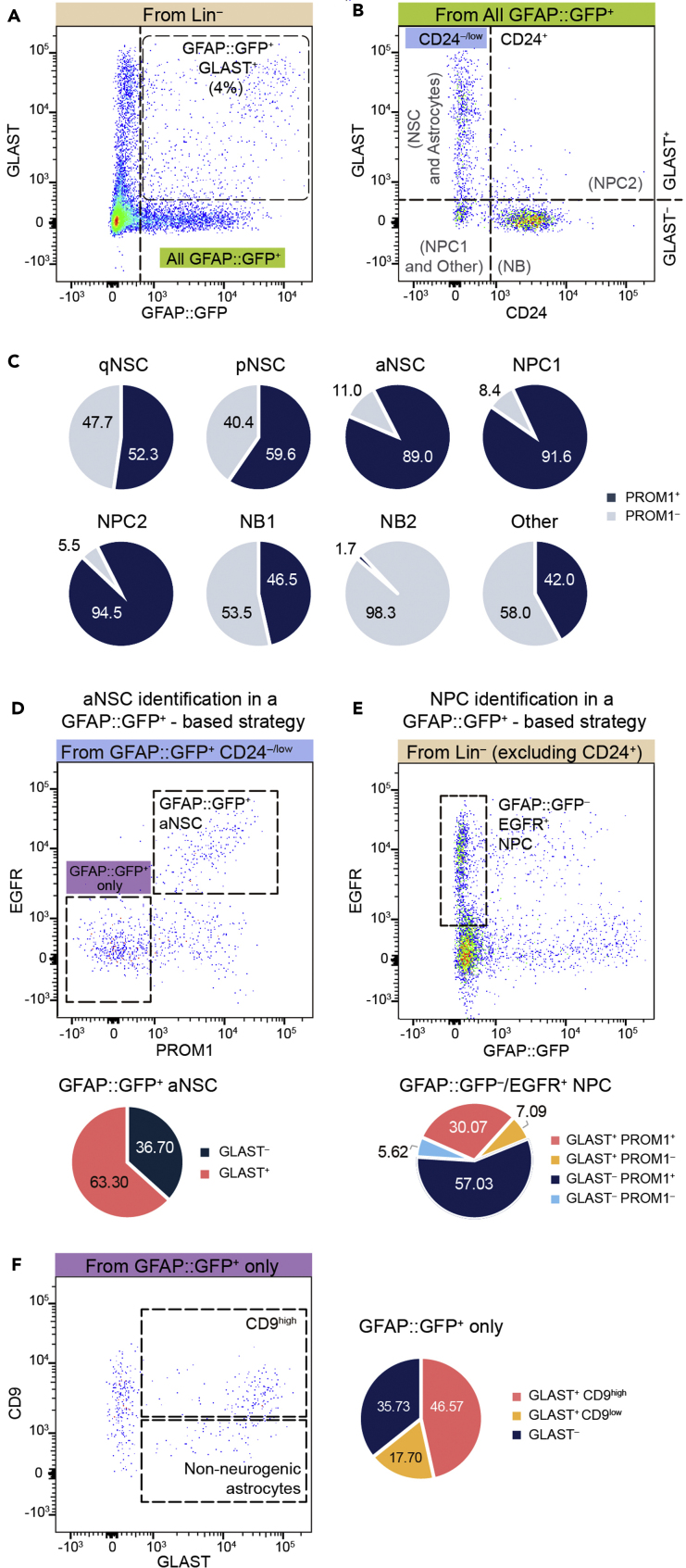
Figure 3.
Comparison between GLAST and GFAP::GFP-based identification of SEZ NSCs and NPCs
(A) GFAP::GFP reporter expression and GLAST immunostaining of SEZ Lin– cells.
(B) GLAST and CD24 expression in the GFAP::GFP+ fraction.
(C) Quantification of PROM1+ cells present in the different SEZ cell types identified (n = 3).
(D) Gating strategy for aNSC and qNSC identification as in Codega et al. (Codega et al., 2014), and quantification of GLAST– GFAP::GFP+ aNSCs (n = 3).
(E) Gating strategy for NPC identification similar to Dulken et al. (Dulken et al., 2017), and distribution of GFAP::GFP– EGFR+ NPCs based on GLAST and PROM1 expression (n = 3).
(F) Representative FACS plot showing the GLAST and CD9 immunostaining of GFAP::GFP-only cells identified in panel D and distribution of GFAP::GFP+ PROM1– astrocytes based in GLAST and CD9 expression (n = 3).