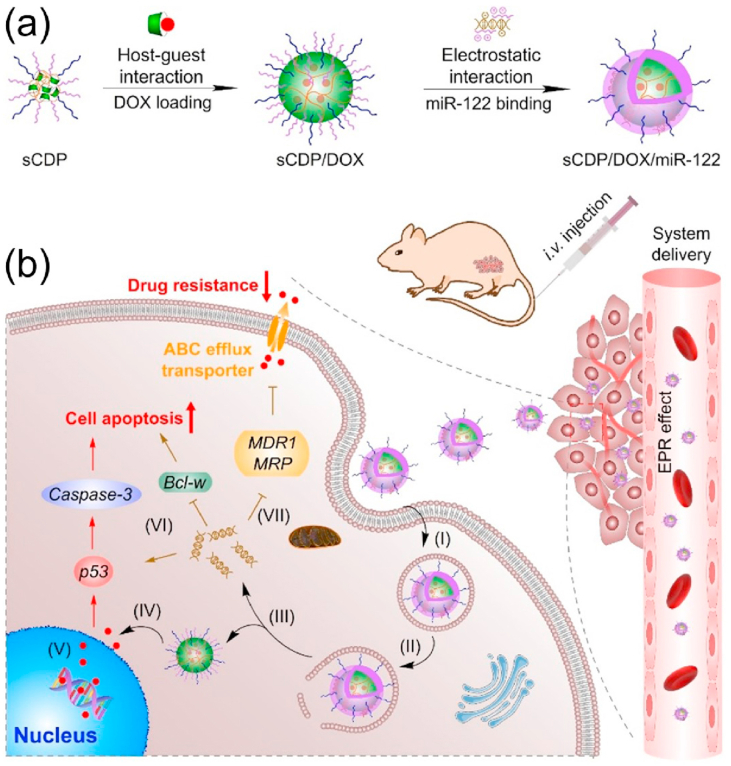
Scheme 1.
Schematic illustration for (a) preparation and (b) effect mechanism of sCDP/DOX/miR-122 in HCC treatment. After intravenous administration, sCDP/DOX/miR-122 enters the blood circulation, extravasates from leaky tumor vasculature, and accumulates at the tumor site. After uptake by HCC cells (I) and endosomal escape (II), sCDP/DOX/miR-122 sequentially releases miR-122 (III) and DOX (IV) into the cytoplasm. DOX enters the cell nucleus and induces DNA damage (V), and miR-122 directly induces cell apoptosis (VI) and decreases drug resistance by inhibiting DOX efflux transporter expression (VII), thus resulting in synergistic anti-tumor effect towards hepatoma.