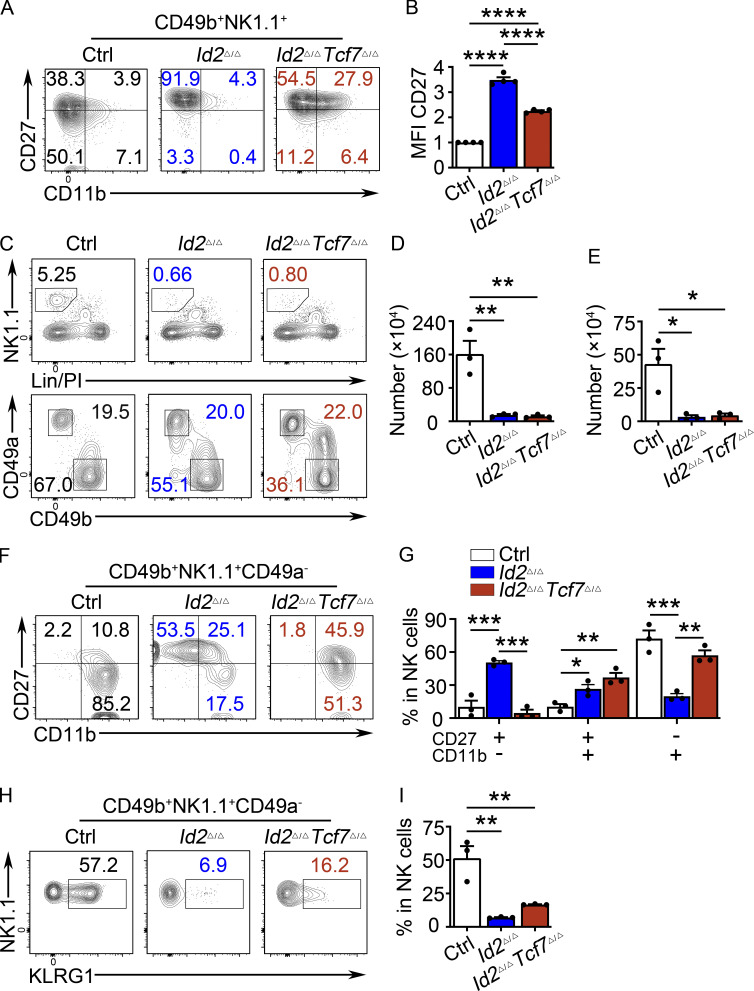
Figure S3.
TCF1 deficiency partially rescues ID2-deficient NK cell maturation in the BM and liver. (A) CD49b+-enriched NK cells from BM were culture in 20 ng/ml IL-15 for 6 d, after which NK1.1+CD49b+ cells were analyzed for CD27 and CD11b by flow cytometry. Numbers indicate the percentage of cells in the respective quadrant (n > 4 from independent experiments). (B) Summary of CD27 MFI for n = 4 in A. MFI of Ctrl NK cells was set as 1 in each experiment. (C) Liver from Id2Δ/ΔTcf7Δ/Δ, Id2Δ/Δ, and Ctrl mice were analyzed by flow cytometry for NK and ILC1 cells. The top panels were from lymphocyte gate, and the bottom panels were from lineage (Lin)/PI−NK1.1+ gate. NK cells are defined as NK1.1+CD49b+CD49a−, and ILC1 cells are defined as NK1.1+CD49b−CD49a+. Numbers are the percentage of cells in the indicated gates (n = 3 from three independent experiments). (D and E) Summary of data shown in C for NK cell and ILC1 cell numbers per 108 cells. (F) NK1.1+CD49b+CD49a− NK cells from the liver were analyzed by flow cytometry for CD27 and CD11b. Numbers indicate the percentage of cells in the respective quadrant (n = 3 from three independent experiments). (G) Summary of data shown in F for frequencies of different NK cell subsets. (H) Flow cytometry plots of KLRG1 expression in Id2Δ/ΔTcf7Δ/Δ, Id2Δ/Δ, and Ctrl mice. Numbers indicate the percentage of cells in the respective quadrant (n = 3; data are from independent experiments). (I) Summary of data shown in H. Error bars represent SEM. Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test (B, D, E, and G) and Holm-Sidak’s multiple comparisons test (I). *, P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.005; ****, P < 0.001.