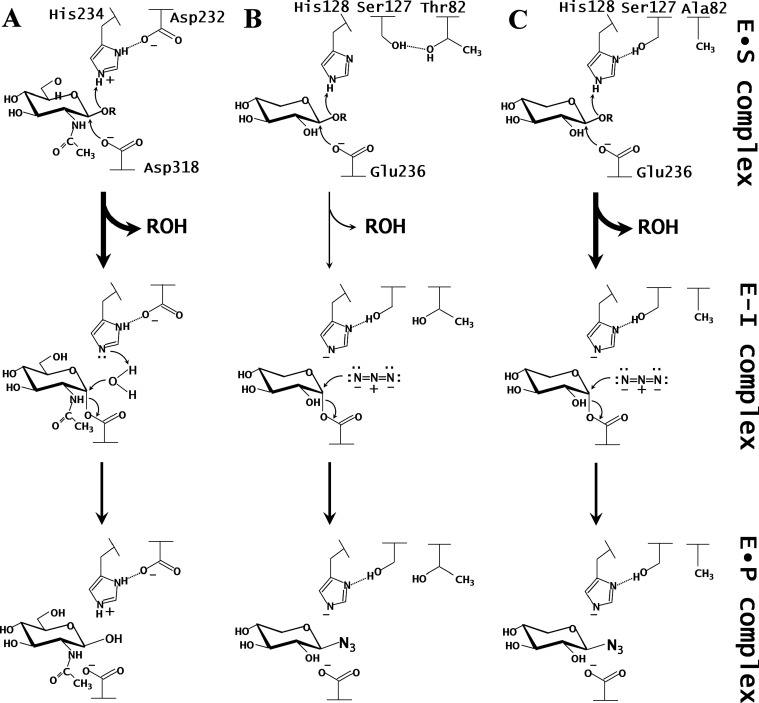
Fig. 1. Proposed reaction mechanisms of the glycosylation of BsNagZ (A), SEA (B), and T82A-SEA (C).
T82A-SEA and SEA15) contain a Ser–His pair, and BsNagZ11) contains an Asp–His catalytic dyad at their active sites. In both cases, the histidine residue serves as an acid catalyst during the glycosylation step. E•S complex, Michaelis complex; E–I complex, covalent glycosyl–enzyme intermediate; E•P complex, enzyme–product complex.