Fig. 4. Lung PD1HiFR4Hi CD4+ T cells are tissue resident.
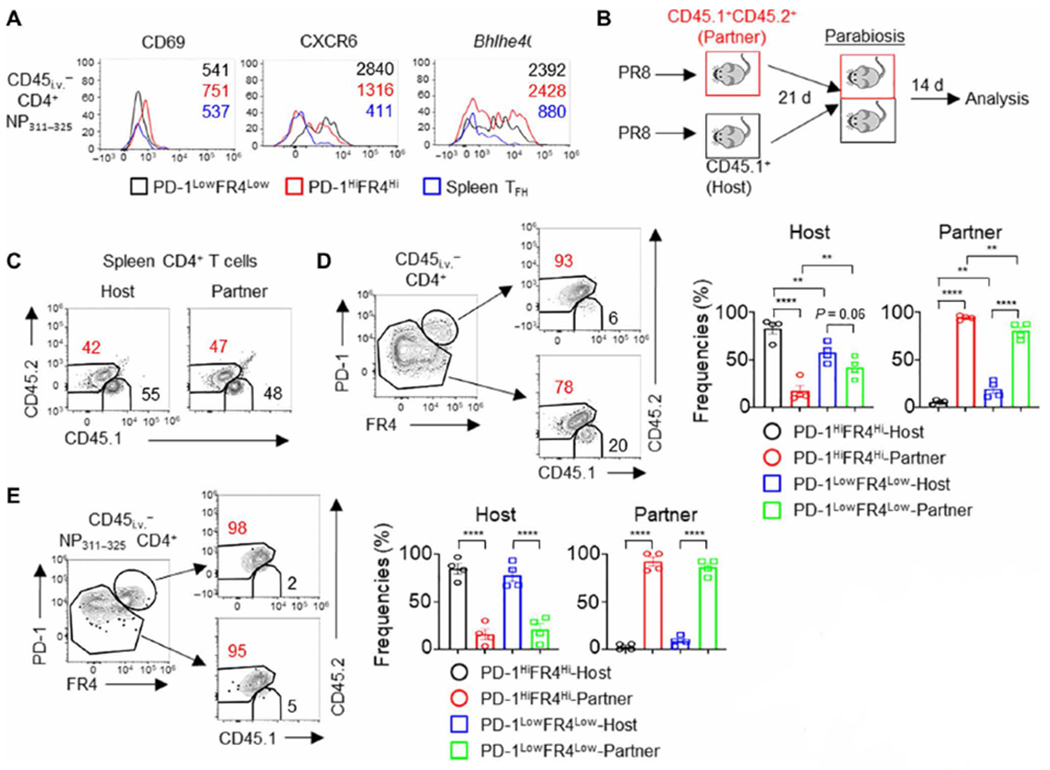
(A) WT mice were infected with PR8. The expression of CD69, CXCR6, and Bhlhe40 in lung CD4+ PD-1HiFR4Hi, CD4+ PD-1LowFR4Low NP311–325 T cells, or splenic TFH cells at 28 d.p.i. (B to E) CD45.1+ (host) or CD45.1+ CD45.2+ (partner) WT mice were infected with PR8. Parabiosis surgery was performed at 21 d.p.i. Mice were euthanized 14 days later for analysis. (B) Schematic of parabiosis experiments. (C) Composition of Host-derived or Partner-derived CD4+ T cells in the spleen of the parabionts. (D) Frequencies of Host-derived or Partner-derived cells in the lung PD-1HiFR4Hi or PD-1LowFR4Low total CD4+ T cell compartment. (E) Frequencies of Host-derived or Partner-derived cells in influenza-specific lung CD4+ PD-1HiFR4Hi or CD4+ PD-1LowFR4Low NP311–325 T cell compartment. In (A), the representative histograms were from at least two independent experiments (three to four mice per group). In (C) to (E), parabiosis data were pooled from two different experiments. P values were calculated by one-way ANOVA in (D) and (E). Data are means ± SEM. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001.
