Fig. 1.
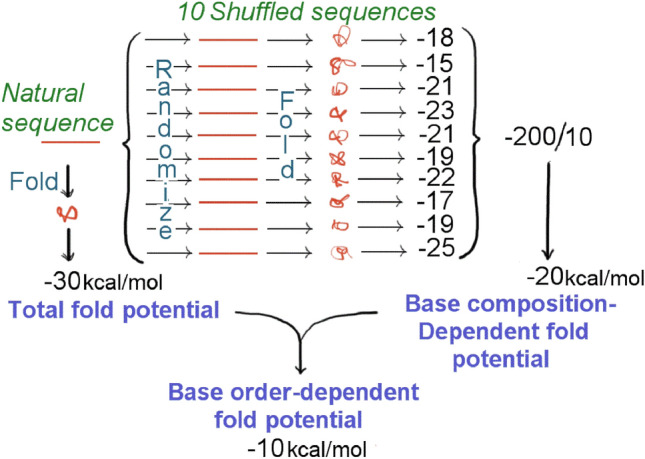
Determination of the base order-dependent component of stem-loop (fold) potential by subtracting the base composition-dependent component from total stem-loop potential. A natural sequence (horizontal red line at left) when optimally folded (vertical arrow at left) is calculated to have a certain stability (e. g. − 30 kcal/mol). Its base order is then randomized to produce ten shuffled sequences that share only their base compositions with the originating natural sequence. These are then optimally folded to obtain corresponding stability values. Idiosyncrasies, due to the base order that each randomized sequence has acquired due to the shuffling, are averaged out (at right) to determine the contribution of base composition to the total fold potential. The contribution of base order is determined by subtraction. This figure is with permission
reproduced from Forsdyke (2016)
