Figure 3. PHENSIM proteomic pathway analysis in SARS-CoV-2-infected human host cells.
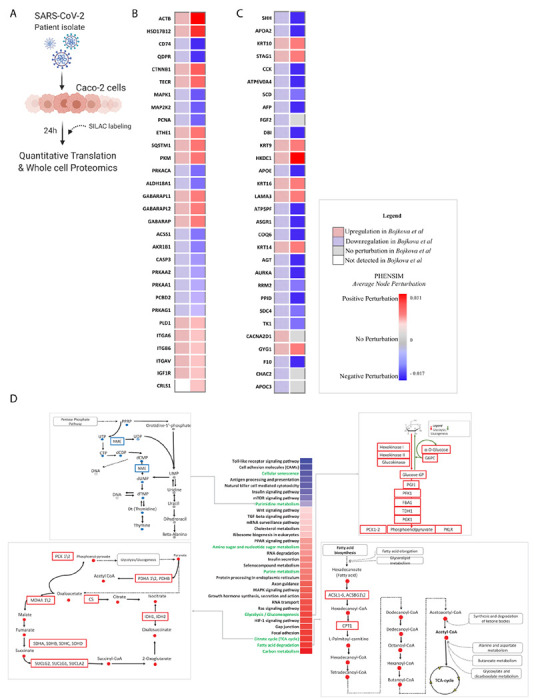
PHENSIM pathway analysis of the Caco-2 cell experiment was simulated in silico to reproduce in vitro results presented by Bojkova et al. at the 24hour time-point post SARS-CoV-2 infection A) Schematic representation depicting the experimental design as described by Bojkova et al. in vitro: the human colon epithelial carcinoma cell line, Caco-2 cells, were infected and monitored for 24hrs post SARS-CoV-2 infection. Naturally occurring heavy isotype SILAC labelling was used to quantify translational changes, as this method does not affect cellular behavior allowing for unbiased pathway analysis. Quantitative translation and whole cell proteomics by LC-MS/MS was performed 5. B&C) Heatmaps depicting a representative subset of the 30 top differentially expressed proteins (FDR<0.05) involved in viral infection after 24hr SARS-CoV-2 infection B) as predicted by PHENSIM in silico (right column, solid squares), compared to expression results as determined by Bojkova et al. (left column, checkered squares) and C) as described by Bojkova et al. (left column, checkered) with side-by-side PHENSIM expression prediction for that protein (right column, solid). D) Heatmap depicts PHENSIM simulated results in silico for the top 30 signaling pathways significantly affected at 24h post infection; Up- (red) and Down-regulated (blue). Pathways depicted in green text are signaling pathways described as significant by Bojkova et al. in their analysis. A select simplified KEGG-based pathways are highlighted on protein interaction level, displaying upregulated proteins in red and downregulated proteins in blue. Color gradient reflects PHENSIM activity; the value of the activity score attributed to each pathway from blue (downregulation) to red (maximum upregulation). Caco-2; the human colon epithelial carcinoma cell line, SILAC; Stable Isotype Labeling by Amino Acids in Cell culture, LC-MS/MS; Liquid chromatography mass spectrometry, DEPs; Differentially expressed proteins, Max; maximum.
