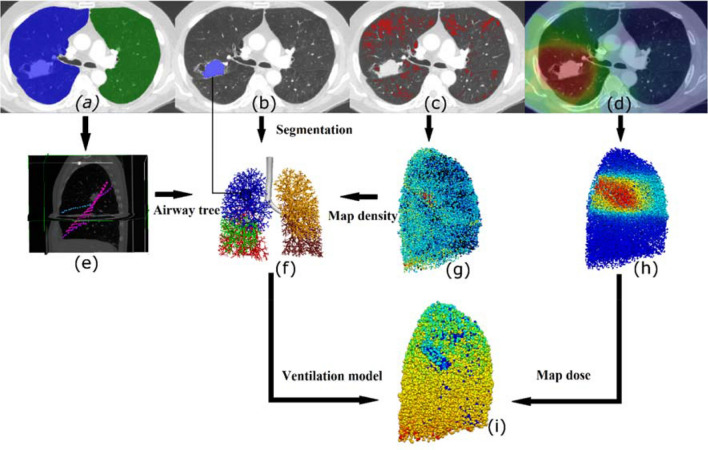
Figure 1.
Illustration of the workflow for creating patient-based models. (a-d)Segmentation of patient CT scans provided: (a) left and right lung volumes, (b) gross tumour volume (GTV), and (c) emphysematous tissue. The dose distribution (d) was overlaid on the CT images. (e) Fissures were manually extracted, and (f) airway trees were grown into patient-based lobar volumes. The GTV was mapped onto the model and airways within the GTV were partially constricted. (g) Emphysema and (h) dose (colour spectrum indicates dose ranging from 0 Gy dark blue to 20 Gy light blue, and 65 Gy red) were mapped from CT onto the airway model. (i): Side view of one patient-based (left lung) model indicating normalised ventilation solution (ventilation/mean ventilation in the whole lung) including constriction due to patient’s tumour (colour indicates normalised ventilation ranging from 0 dark blue to 1.5 red).