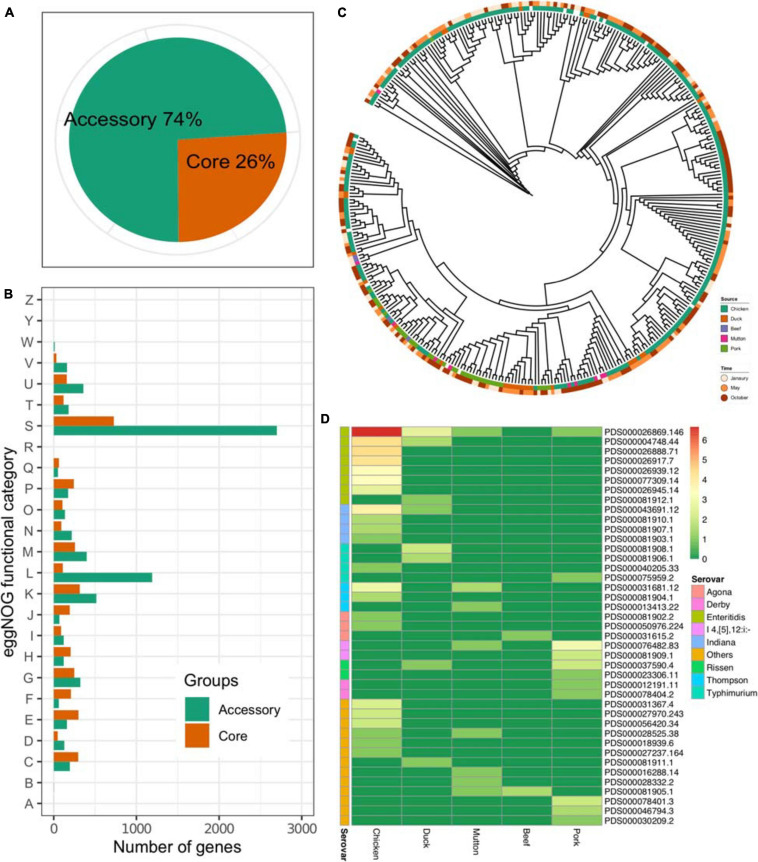
FIGURE 2.
Core genome of Salmonella. (A) Proportions of accessory genes and core genes in the pangenome. (B) Core and accessory genome functional annotation. RNA processing and modification, A; chromatin structure and dynamics, B; energy production and conversion, C; cell cycle control, cell division, chromosome partitioning, D; amino acid transport and metabolism, E; nucleotide transport and metabolism, F; carbohydrate transport and metabolism, G; coenzyme transport and metabolism, H; lipid transport and metabolism, I; translation, ribosomal structure and biogenesis, J; transcription, K; replication, recombination and repair, L; cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis, M; cell motility, N; posttranslational modification, protein turnover, chaperones, O; inorganic ion transport and metabolism, P; secondary metabolites biosynthesis, transport and catabolism, Q; general function prediction only, R; function unknown, S; signal transduction mechanisms, T; intracellular trafficking, secretion, and vesicular transport, U; defense mechanisms, V; extracellular structures, W; nuclear structure, Y; cytoskeleton, Z. (C) An ML tree constructed based on the core SNPs (n = 277,664). (D) Prevalence of the SNP clusters from different sources. Color: the number of the isolates (log2-transformed).