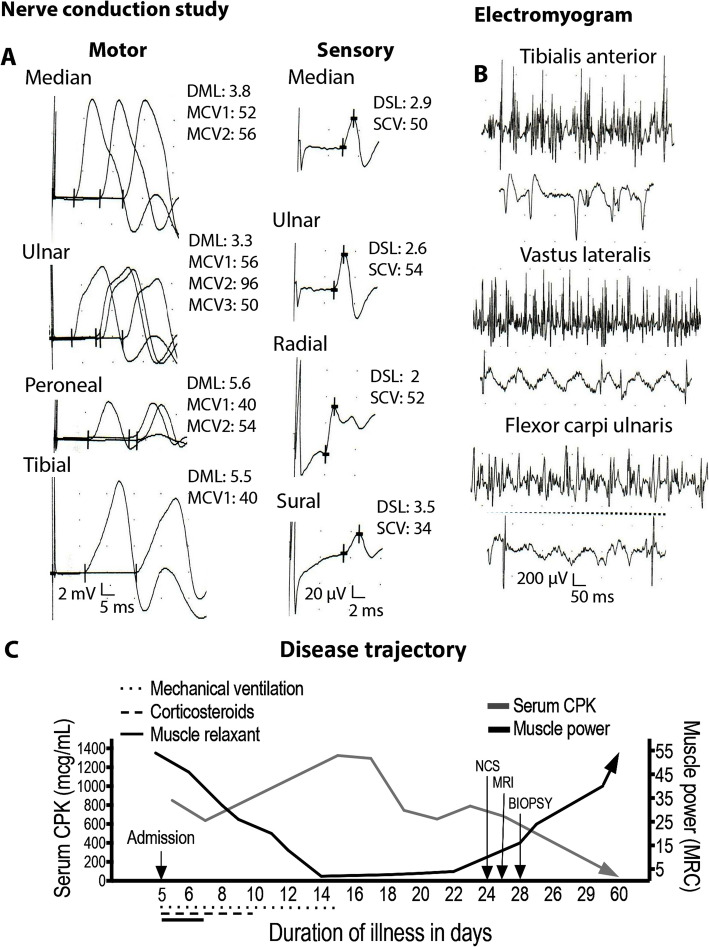
Fig. 1.
Nerve conduction study, electromyogram, and disease trajectory. (a) Motor and sensory nerve conduction was normal despite severe muscle weakness. Compound muscle action potential (CMAP) amplitudes are measured in millivolts (mV); 2 mV per division for all motor study traces. DML, distal motor latency in ms. MCV1, motor conduction velocity in millisecond (ms). MCV2, motor conduction velocity in ms. Sensory nerve action potential (SNAP) amplitudes are measured in microvolts (μV); 20 μV per division for all sensory study traces. DSL, distal sensory latency. SCV, sensory conduction velocity. (b) Electromyogram (EMG) showing myopathic motor unit potentials, a full recruitment pattern and spontaneous muscle fiber activity in several sampled muscles. Motor unit potential (MUP) amplitudes are measured in microvolt (μV); 200 μV per division for all EMG traces