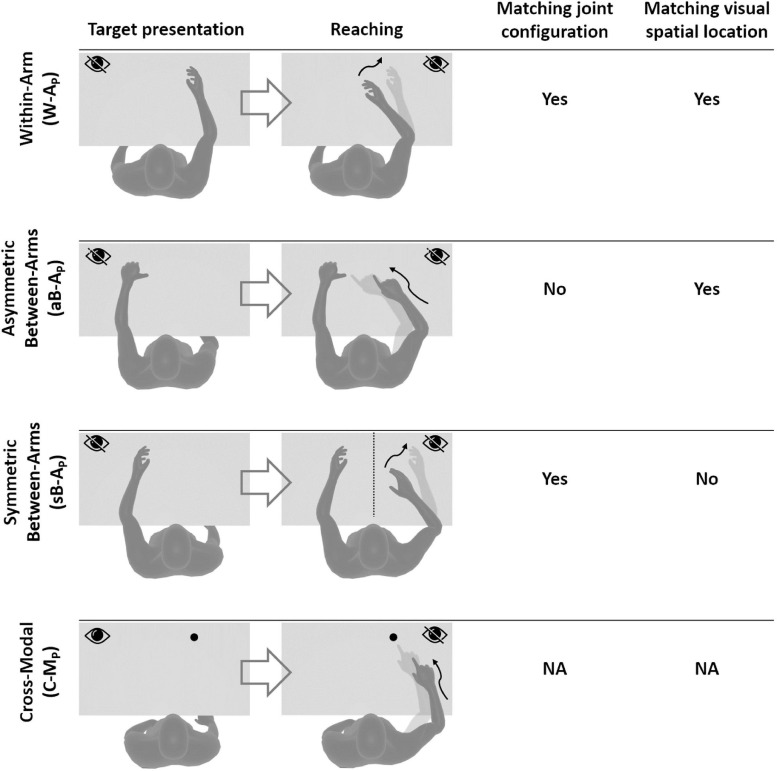
FIGURE 1.
Four categories of proprioceptive assessments. In all represented examples, subjects are asked to, first, perceive a target position and then to reach for it. The last two columns show that the tasks categorization is based on the possibility, or not, to compare the target and effector position in joint and/or retinal space. In the within-arm category (W-A) the patient first perceives and then moves back to the target with the same arm. In the asymmetric between-arms category (aB-A) the location of the target perceived with one hand is subsequently reached with the other hand. In the symmetric between-arms category (sB-A) the patient perceives the target with one hand and mirrors its position with the other hand. In the cross-modal (C-M) category, where the hand and the target do not share the same sensory modality, the patient reaches for a visually memorized target with the unseen hand.