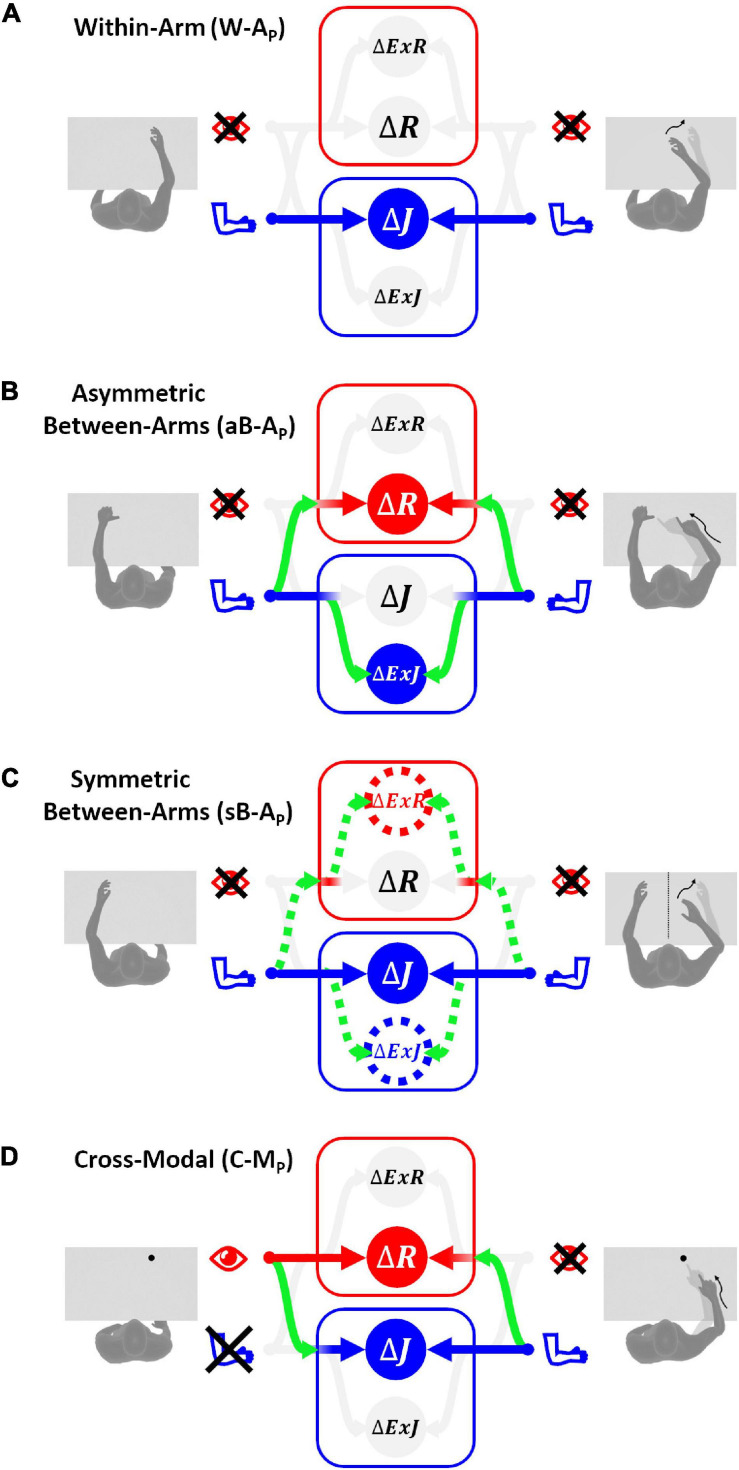
FIGURE 4.
Sensory information flow predicted for proprioceptive tests. The model results are reported separately for the four categories of tests without vision of the arms: (A) within-arm task (W-AP), proprioceptive joint signals from the right arm during the target memorization (left column) can be directly compared with proprioceptive joint signals from the same arm during the response phase (right column). (B) Asymmetric between-arms task (aB-AP), the task cannot be achieved by simply matching the homologous proprioceptive joint signals from the left and right arm: the use of alternative reference frames and cross-reference transformations (green curved arrows) is necessary. (C) Symmetric between-arms task (sB-AP), proprioceptive joint signals from the left arm during the target memorization can theoretically be compared directly with the homologous proprioceptive joint signals from the right arm. However, for patients with inter-hemispheric transformation impairment, indirect comparisons (doted lines) are necessary. (D) Cross-modal task (C-MP), the target and the effector do not share the same sensory modality. The model prediction in this situation consists in encoding the task in both joint and retinal space by performing the depicted cross-reference transformation. The target-effector comparisons performed in a sensory space associated with a weight close to zero are in pale gray, while those associated with weights significantly larger than zero are in bright colors.