Figure 2. Multiple LLPS modules play a role in signaling in dendritic spines.
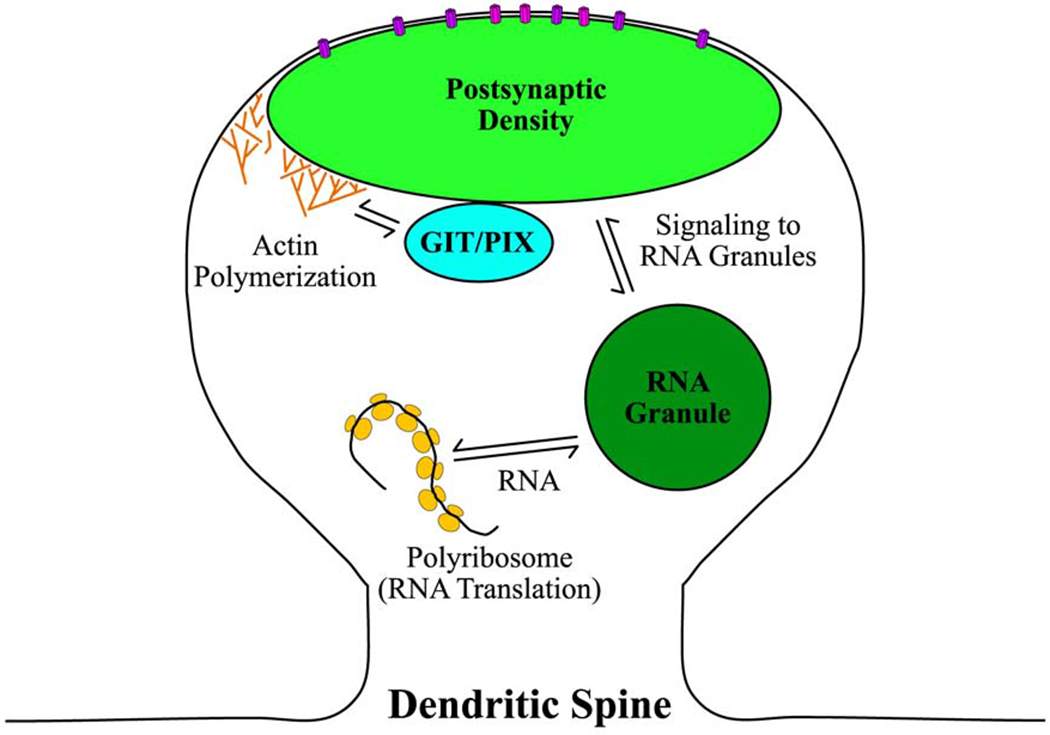
The PSD is a protein-rich condensate that resides at the plasma membrane in dendritic spines. Phase separation of core PSD proteins controls NMDAR (magenta) and AMPAR (violet) localization on the dendritic spine membrane. Binding of neurotransmitters to these receptors initiates signaling pathways to control local actin polymerization and RNA translation. Phase separated GIT/PIX condensates localize in dendritic spines and coordinate with the PSD to control actin polymerization by regulating Rho GTPases [38]. Both GIT/PIX and PSD condensates contain actin regulatory proteins, suggesting that they can simultaneously contribute to controlling local actin polymerization. Signaling in dendritic spines also triggers RNA granules, another condensate that localizes to dendritic spines, to process translationally repressed RNA [58]. The processed RNA can then be translated by polyribosomes in dendritic spines.
