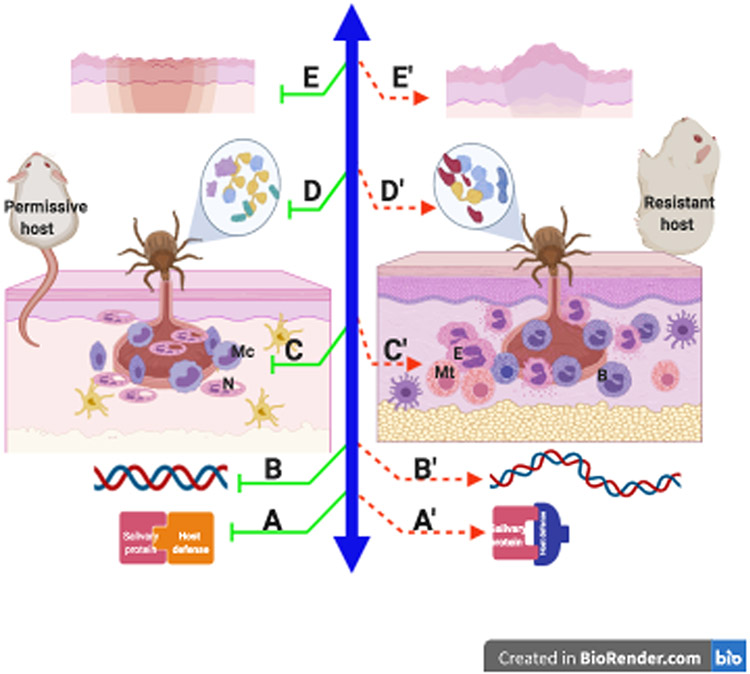
Figure 2. Potential mechanisms of acquired tick resistance.
Factors that may drive the dichotomous immune responses to tick bites on permissive or resistant host species include: Optimal (A) or suboptimal (A’) engagement of salivary proteins with host defense responses; genetic predisposition to decreased (B) or increased (B’) inflammatory responses to salivary proteins; structural and immunological differences in the skin (C, C’); Host-specific salivary proteome that is sufficient (D) or deficient (D’) in modulating host defense responses; and differences in wound healing without scar (E) or with scar (E’) formation.