Figure 2: Interactions between B. burgdorferi and the Ixodes tick vector.
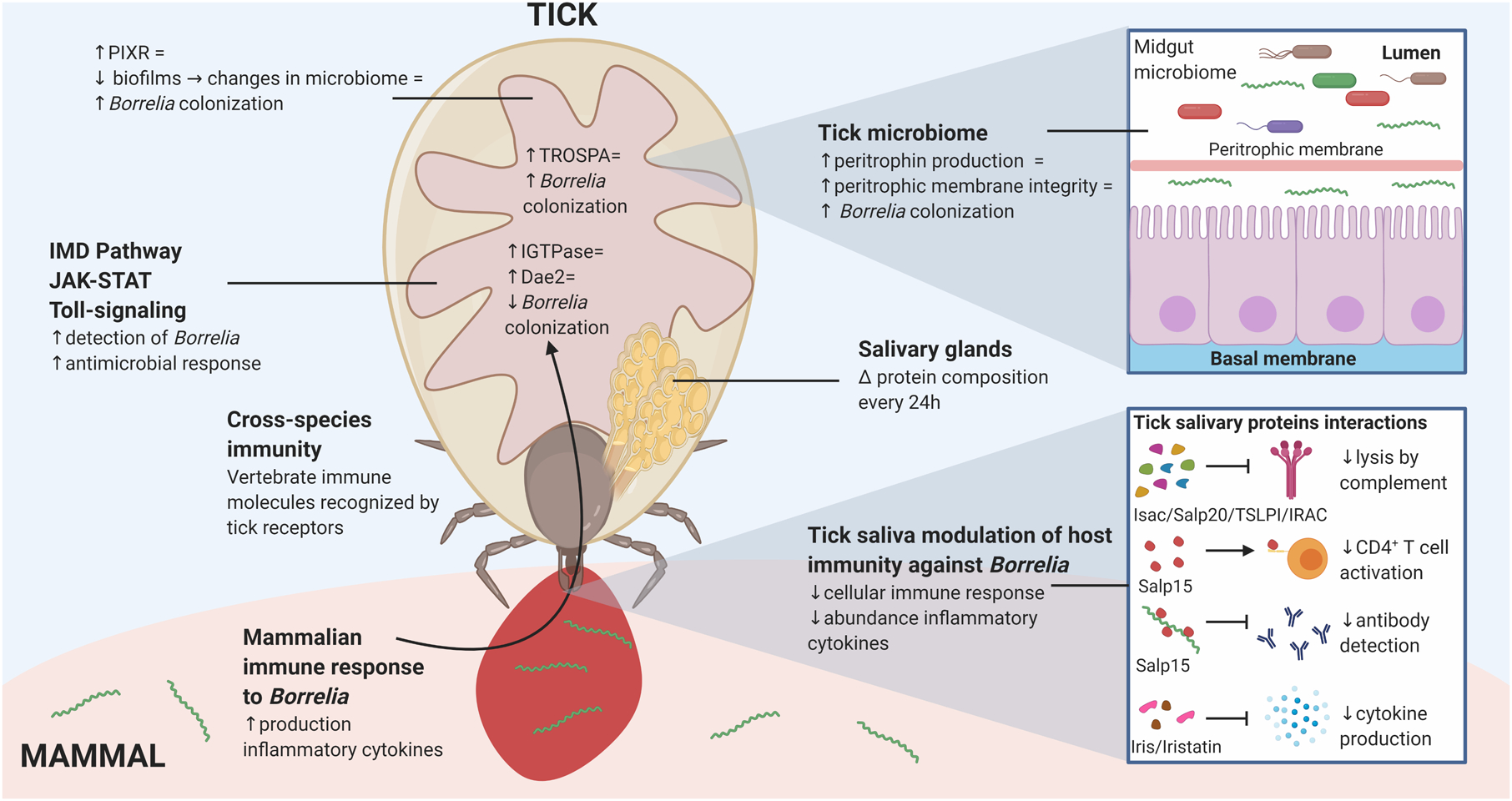
Interactions between B. burgdorferi and tick proteins occur at multiple locations within the tick. The tick midgut provides an opportunity to influence B. burgdorferi colonization through the peritrophic membrane, tick gut microbiome, and other tick gut proteins, including TROSPA and PIXR. Tick salivary gland proteins are able to impair the mammalian immune response and aid B. burgdorferi survival within the mammal. Some of these interactions include Isac, Salp20, TSLPI and IRAC prevention of complement mediated lysis of B. burgdorferi, Salp15 binding to CD4+ T cells and inhibiting their activation, while simultaneously binding to B. burgdorferi and preventing antibody mediated detection of the spirochete, and Iris and Iristatin mediated reduction of proinflammatory cytokine production. The equal sign denotes “leads to.” Created with BioRender.com.
