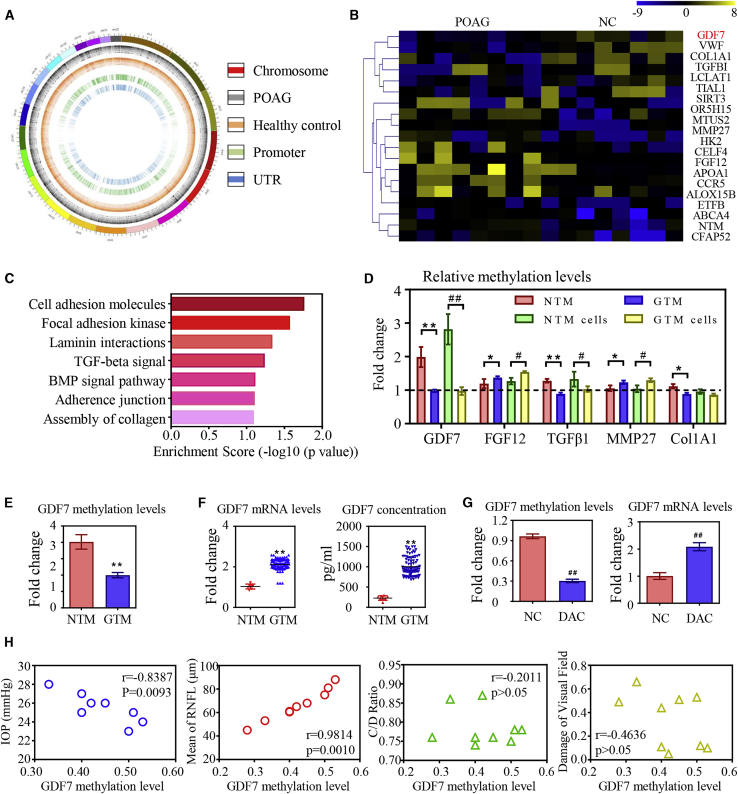
Figure 1.
GDF7 hypomethylation was the crucial event in glaucoma
(A) Diagram of aberrantly methylated regions in primary open angle glaucoma (POAG). From the outside in, the first layer presents the chromosomal information; the second and third layers present the different methylation sites in POAG patients and healthy controls (CONs), respectively; and the fourth and fifth layers present aberrantly methylated promoters and untranslated regions (UTRs) in POAG patients. (B) The top 20 differentially methylated sites in glaucomatous trabecular meshwork (GTM) samples (presented in reference name). As normalized to the controls, the relative methylation levels of the target regions were represented in the pseudocolor (n = 8 per group). (C) The disrupted methylation genes in POAG patients enriched in seven biological pathways as analyzed by Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG). (D) The dysregulated methylation levels of five candidates were confirmed by bisulfite sequencing PCR (BSP) in trabecular meshwork (TM) samples and cells (n = 3 per group). (E) Decrease in methylation level of the GDF7 promoter was confirmed in eight GTM samples compared to healthy controls by BSP (n = 8 per group). (F) Ninety GTM samples were obtained from trabeculectomy (clinical information in Table S2) to validate the expression of GDF7 by quantitative real-time PCR and ELISA. Note: the readouts were normalized to the eight normal TM (NTM), due to the limitation of the donations we can get. (G) The GDF7 methylation level in response to 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine (DAC) treatment was tested by BSP, and the change in GDF7 mRNA level was measured by real-time PCR in TM cells (n = 3 per group). (H) Correlation analysis between GDF7 methylation level and clinical manifestations in POAG patients (n = 8). The data represent the mean ± SD. Compared with NTM samples: ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01. Compared with NTM cells: #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01. NC, normal control; IOP, intraocular pressure; CDR, cup/disc ratio; RNFL, retinal nerve fiber layer.