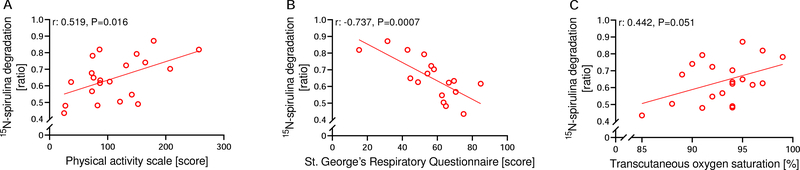
Figure 5:
Correlations between 15N-spirulina degradation ratio, a marker of protein digestion and absorption, and different clinical parameters related to Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). Patients with a higher 15N-spirulina degradation ratio reported a higher physical activity level (A; n=21), a higher quality of life (B; n=17), and tended to have a higher transcutaneous oxygen saturation (C; n=20).