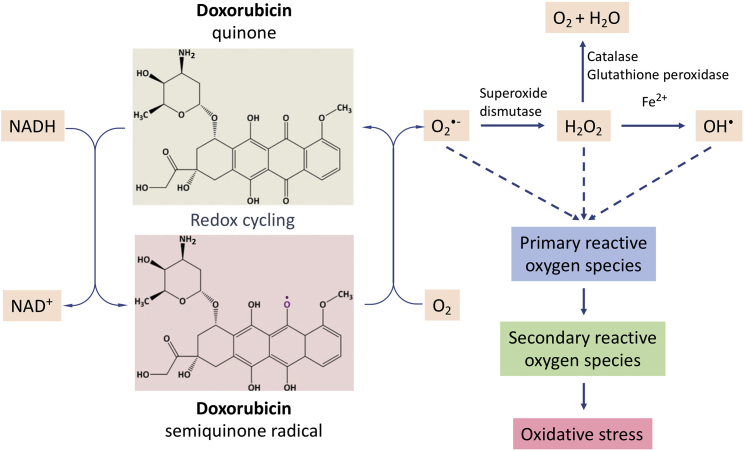
Figure 1.
Redox cycling of doxorubicin in the mitochondria
Doxorubicin is bioactivated by complex I of the mitochondrial respiratory chain at the expense of NADH. This is followed by the rapid re-oxidation of the semiquinone radical in the presence of molecular oxygen to generate superoxide anion-free radicals. Subsequently, further primary reactive oxygen species and secondary reactive oxygen species are produced, leading to oxidative stress.