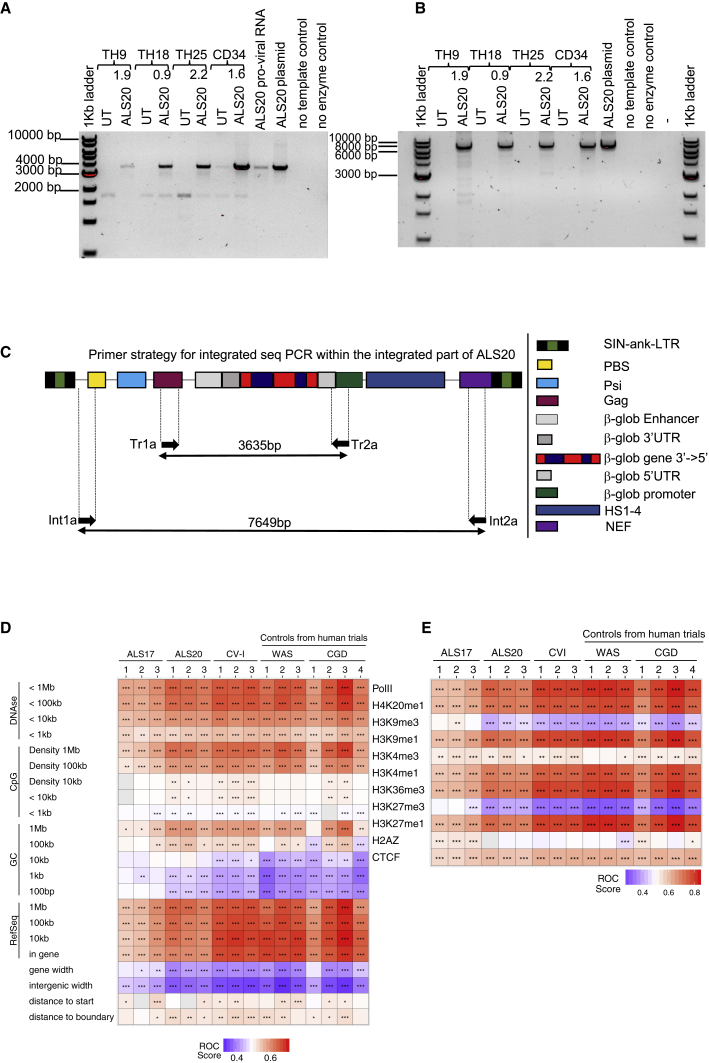
Figure 3.
Viral genome and transgenic cassette stability after integration and polyclonality
(A) Representation of amplicons obtained after semiquantitative PCR of genomic DNA isolated from primary beta0beta0 erythroblasts, human CD34+ cells transduced with ALS20, and from control ALS20 plasmid and proviral cDNA using the Tr1A and Tr2A primer set, which amplifies a 3.63-kb transgenic region within ALS20. (B) Representation of amplicons obtained after semiquantitative PCR of genomic DNA isolated from primary beta0beta0 erythroblasts, human CD34+ cells transduced with ALS20, and from control ALS20 plasmid using the Int1A and Int2A primer set, which amplifies the 7.6-kb cassette that is included between the viral long terminal repeats. (C) Schematic representation of the viral components and location of the primers designed to amplify the regions obtained in (A) and (B). (D and E) Representative heatmaps summarizing the distribution sites of integration relative to the genomic features or mapped sites of epigenetic modifications or bound proteins, respectively, in human hematopoietic stem cells. The distribution of lentiviral vector integration sites were compared with the distribution of random sites using the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve method.30 The columns indicate the sample analyzed. Data from samples transduced with ALS20, ALS17, and CV-I (three biological replicas per vector) were analyzed with samples from patients treated safely in clinical trial for Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome (WAS) and chronic granulomatous disease (CGD). (D) The rows indicate comparisons to genomic feature annotations that are mapped on the human genome (hg38). Associations are quantified as ROC areas, which compare experimental integration site sets to computationally generated random distributions. Values are color coded on each tile and range between 0 (negatively associated; blue) and 1 (positively associated; red). The most appropriate chromosomal interval for comparison is not known in advance, so multiple intervals were used. p values were calculated using the Wald test using a chi-square distribution; no correction for multiple comparisons was applied. p values are marked on the heatmap tiles: ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001. RefSeq.counts indicate comparisons based on the RefSeq gene numbers in the indicated intervals; gene.width indicates the width of genes containing integration sites; general.width indicates the width of intergenic regions that host integration sites; start.dist shows comparisons based on distances to transcription start sites; and boundary.dist indicates comparisons based on distances to gene boundaries. (E) Similar to what is presented in (D) but with comparisons of integration site distributions and random distributions relative to mapped epigenetic marks and sites of bound proteins in human hematopoietic stem cells. All comparisons used 10-kb intervals.