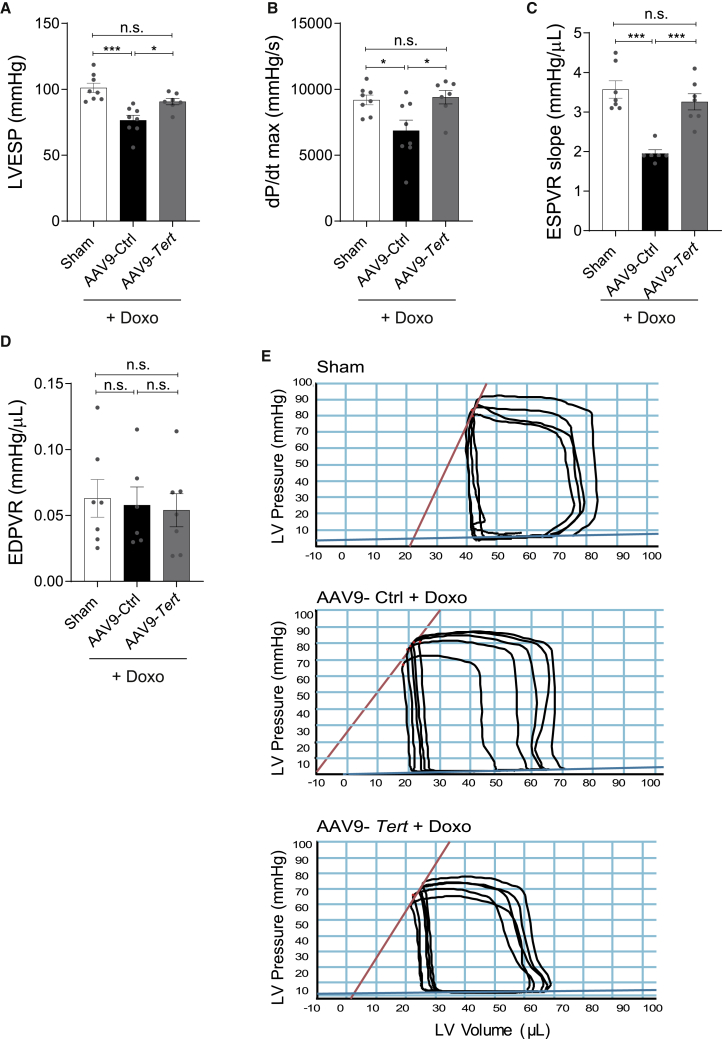
Figure 3.
Effect of AAV9-mediated Tert overexpression on doxorubicin-induced systolic dysfunction
(A–E) Measures of global systolic function (LVESP and dP/dT) (n = 8/8/7 mice) (A and B); load-independent systolic and diastolic parameters (ESPVR, EDPVR) (n = 7/6/7 mice) (C and D); and representative pressure-volume (PV) loops (E) obtained with a PV conductance catheter system at varying preload using transient vena cava occlusion, showing differences between mice injected with AAV9-Tert or control virus and then treated with saline or doxorubicin. AAV9 particles were injected at a dose of 1 × 1012 vg/mouse. LVESP, left ventricular end-systolic pressure; dP/dt max, ventricular contractility assessment; ESPVR, end-systolic pressure volume relationship; EDPVR, end-diastolic pressure volume relationship. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001; one-way ANOVA, Tukey multiple-comparisons test.