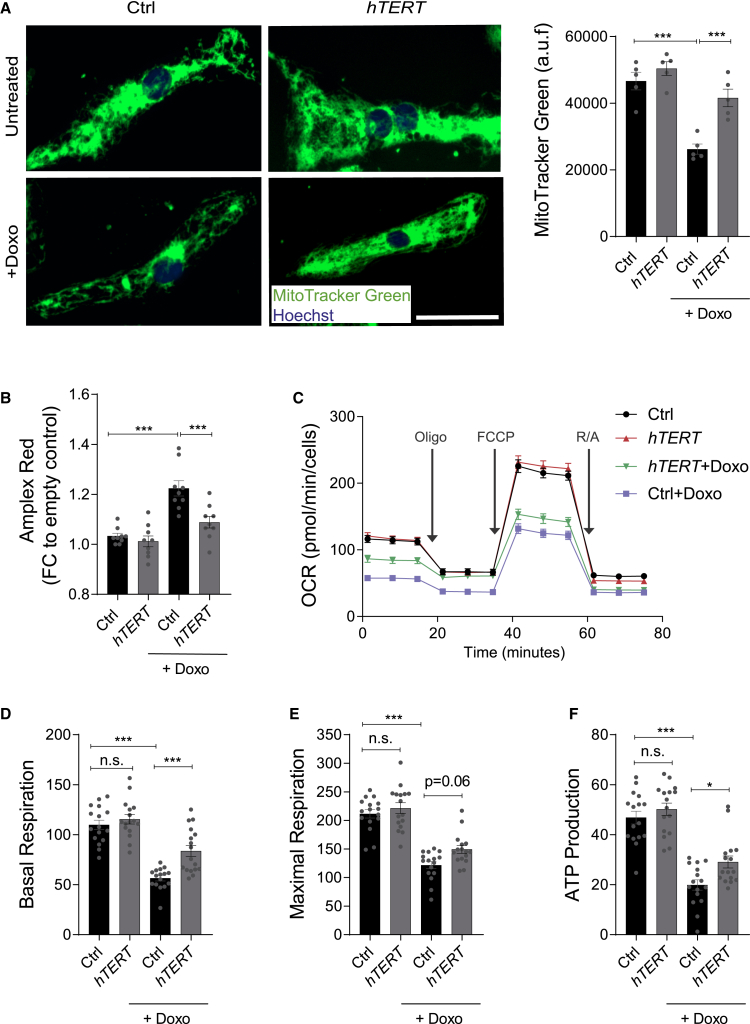
Figure 7.
AAV6-hTERT protects from ROS and preserves mitochondrial metabolism post doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity
(A) HiPSC-CMs overexpressing hTERT stained with MitoTracker Green FM in presence and absence of doxorubicin (1 μM, 48 h) and compared to control group. The fluorescence signal of MitoTracker Green FM from images on the left are quantified and represented on the right, which indicate mitochondrial content (n = 5 wells/group with 100,000 cells in each well from one differentiation experiment). Scale bar is 50 μm. (B) Bar graph represents the fold change of the extracellular ROS measured by Amplex Red assay before and after doxorubicin treatment in the presence and absence of AAV6-hTERT. The results indicate lower ROS levels after doxorubicin (1 μM) in the presence of hTERT. (n = 9 wells/group from triplicates of 3 independent differentiation experiments). (C) Analysis of hiPSC-CM mitochondrial metabolism using a Seahorse XFe96 Analyzer after transduction with AAV6 hTERT and in presence or absence of doxorubicin (1 μM). OCR was measured continuously at baseline and after addition of oligomycin (2 μM), FCCP (1 μM), and R/A (0.5 μM) (n = 16 wells/group with 50,000 cells in each well from one differentiation experiment). (D–F) The average levels of basal respiration, maximal respiration, and ATP production. The mitochondrial metabolism reduces after doxorubicin treatment, which is rescued by AAV6-hTERT therapy. All data are mean ± SEM. AAV6 transduction performed with 104 MOI. OCR, oxygen consumption rate; oligo = oligomycin; FCCP, carbonyl cyanide-4-phenylhydrazone; R/A, rotenone and antimycin A. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗∗p < 0.001; one-way ANOVA, Tukey multiple-comparisons test.