Fig. 2.
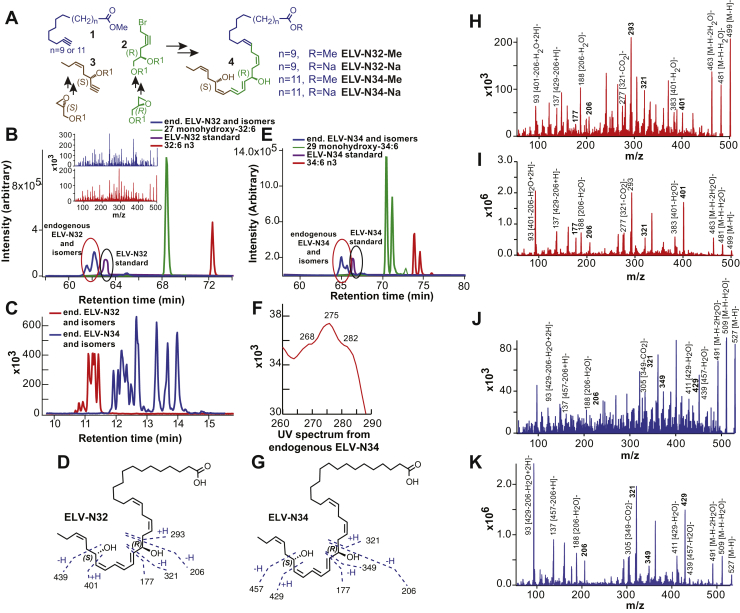
Discovery and structural characterization of ELV-N32 and ELV-N34 in primary human RPE cells in culture. A: ELV-N32 and ELV-N34 were synthesized from three key intermediates (1, 2, and 3), each of which was prepared in stereochemically pure form. The stereochemistry of intermediates 2 and 3 was predefined by using enantiomerically pure epoxide starting materials. The final ELVs (4) were assembled via iterative couplings of intermediates 1, 2, and 3 and were isolated as methyl esters (Me) or sodium salts (Na). B: 32:6n3 (red line), endogenous mono-hydroxy-32:6n3 (green line), and ELV-N32 (blue line) are shown with the ELV-N32 standard (purple). Multiple reaction monitoring of ELV-N32 shows two large peaks eluted earlier than the peak when standard ELV-N32 was eluted, displaying the same fragmentation patterns (shown in the insert spectra), suggesting that they are isomers. C: Chromatogram for full daughter scans for ELV-N32 (red line) and ELV-N34 (blue line). D: Fragmentation pattern of ELV-N32. E: Same features as in (B) for 34:6n3 and ELV-N34. F: UV spectrum of endogenous ELV-N34 showing triene features. G: Fragmentation pattern of ELV-N32. H: Full fragmentation spectra of endogenous ELV-N32 and (I) the ELV-N32 standard shows that all major peaks from the standard match to the endogenous peaks. However, endogenous ELV-N32 has more fragments that do not show up in the standard, suggesting that it includes different isomers. J: For ELV-N34, full fragmentation spectra of endogenous ELV-N34 peaks match up with the standard ELV-N34 (K), also suggesting the existence of ELV-N34 isomers. Reproduced, with permission, from Scientific Reports (25). ELV, elovanoid; RPE, retinal pigment epithelium.