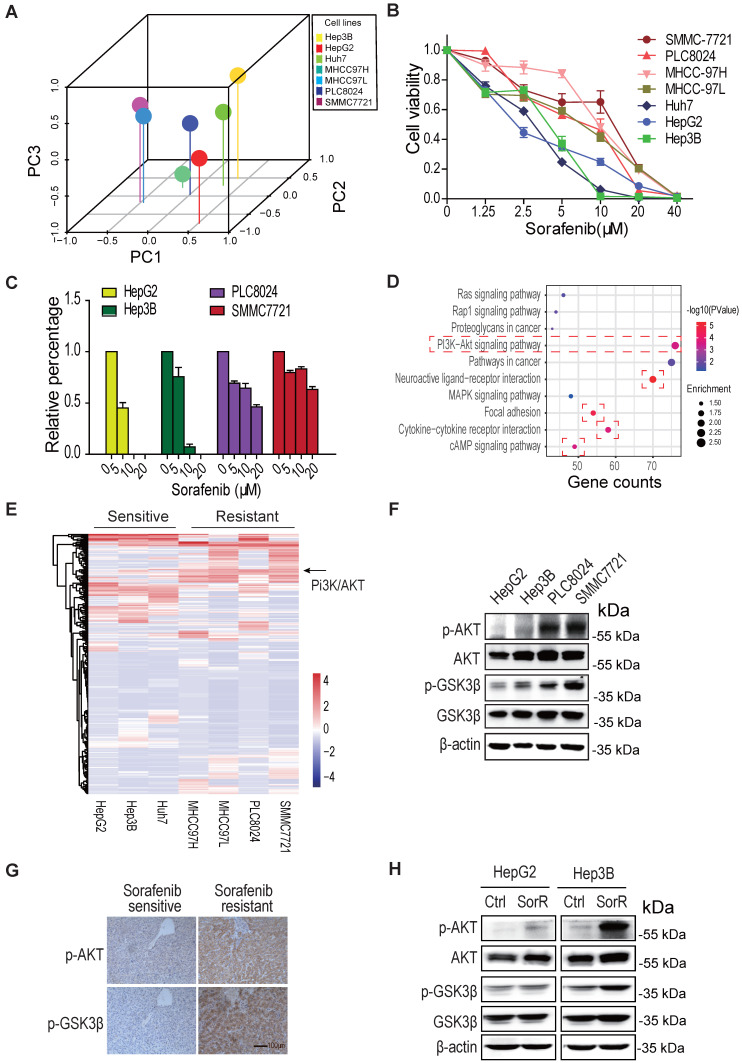
Figure 1.
AKT is activated in sorafenib-resistant hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). A. The principal component analysis (PCA) on various HCC cells. B & C. SMMC7721 and PLC8024 cells are more resistant to sorafenib than HepG2 and Hep3B cells. HCC cells were treated with sorafenib as detailed in Methods and viability was analyzed by the CCK8 method (B) and colony formation assays (C). Data shown are mean ±SD of at least 3 independent experiments. D. The gene ontology analysis on the upregulated/downregulated genes. The RNA-sequencing were performed, the genes whose expression changed more than ± 2 folds in sorafenib-resistant HCC cells were analyzed, compared to sorafenib-sensitive HCC cells. The PI3K/AKT, focal adhesion, cytokine-cytokine receptor, neuroactive ligand-receptor, and cAMP signaling were activated in de novo sorafenib-resistant PLC8024 and SMMC7721 cells. E. The heatmap display of upregulated/downregulated genes among sorafenib-sensitive and sorafenib-resistant HCC cells. The change folds of gene expression were more than ± 2. F. Akt was phosphorylated in de novo sorafenib-resistant PLC8024 and SMMC7721 cells. The T308 phosphorylation of Akt and S9 phosphorylation of GSK3β were analyzed. G. Akt was phosphorylated in sorafenib-resistant HCC tumors. Tumor sections for phospho-AKT and phospho-GSK3β staining in each set were from adjacent slices of same tumor. H. AKT was phosphorylated in acquired sorafenib-resistant HepG2 and Hep3B cells.