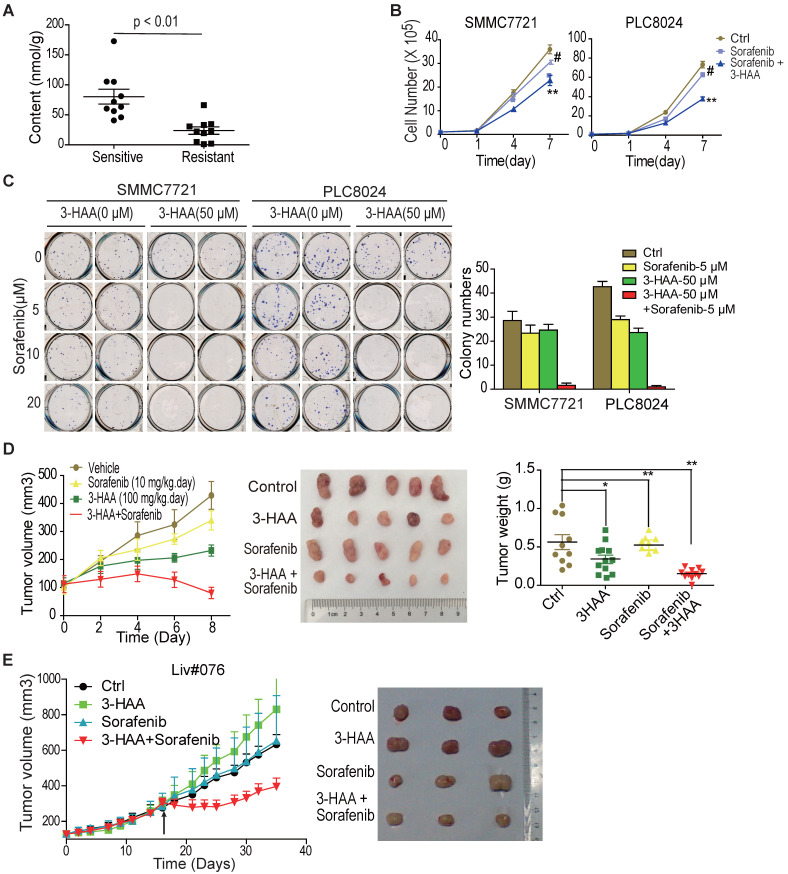
Figure 2.
3-HAA sensitizes HCC to sorafenib both in vitro and in vivo. A. Quantitative analysis of 3-HAA by LC-MS/MS in sorafenib sensitive or resistant HCCs. B. 3-HAA inhibits cell growth of sorafenib-resistant HCC cells. The cell numbers of HCC cells were counted by cytometry. Data shown are mean ± SD of at least 3 independent experiments. C. 3-HAA reduces colony formation in sorafenib-resistant SMMC7721 and PLC8024 cells. The cells were treated with sorafenib at the indicated dose with and without 50 μM of 3-HAA for 4 days. The graphic shows colony numbers as cells treated with 5 μM of sorafenib with or without 50 μM of 3-HAA. Data shown are mean ± SD of at least 3 independent experiments. D. The combination of 3-HAA and sorafenib synergistically suppresses the growth of SMMC7721 xenografts. 3-HAA and the sorafenib were administered by intraperitoneal injection for 7 days at the dose of 100 mg/kg.day and 10 mg/kg.day, respectively. Tumor volumes and tumor weight are presented as mean ± SD (*: P < 0.05; **: P < 0.01.). Five mice were recruited in each group. E. The combined treatment with 3-HAA dramatically suppresses tumor growth of patient-derived sorafenib-resistant HCC xenografts. As xenografts reached at approximately 250 mm3, 3-HAA and the sorafenib were administered by intraperitoneal injection for 14 days at the dose of 100 mg/kg.day and 30 mg/kg.day, respectively. Three mice were recruited in each group.