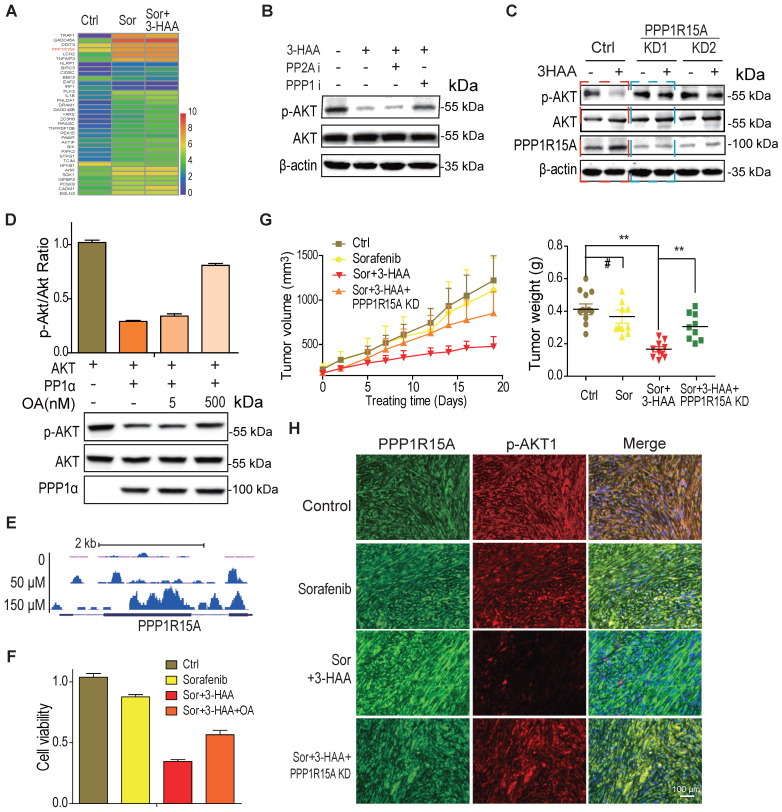
Figure 4.
3-HAA inhibits AKT activity by upregulation of PPP1R15A. A. The genes involved in apoptosis pathway and upregulated by the combination of sorafenib and 3-HAA. The concentration of sorafenib and 3-HAA were 5 μM and 50 μM, respectively. B. The phosphatase PPP1α inhibitor okadaic acid but PPP2A inhibitor Calyculin A restored the AKT phosphorylation in 3-HAA-treated SMMC7721 cells. The dose of both calyculin A and okadaic acid were 2 nM. Cells were treated for 4 h. C. The PPP1R15A knockdown restores AKT phosphorylation suppressed by 3-HAA. The treating time and 3-HAA dose were the same as above. D. The effects of PPP1R15A/PPP1α on Akt phosphatase. The phosphatase assay was described in methods. E. The ChIP-sequencing analysis of YY1 on PPP1R15A gene. F. PPP1α inhibitor Okadaic acid (OA) partially restored the cell survival. The dose of Okadaic acid and the 3-HAA was 2 nM and 100 μM, respectively. Cells were treated for 24 h. G. The combination of sorafenib and 3-HAA dramatically decreased the tumor growth and tumor weights while PPP1R15A knockdown restored the xenograft growth and xenograft weights. Five mice were recruited in each group. H. The combination with 3-HAA treatment upregulated PPP1R15A expression and inhibited Akt activation in SMMC7721 xenografts. As xenografts reached at approximately 100 mm3, the sorafenib and/or 3-HAA were administered by intraperitoneal injection for 14 days at the dose of 100 mg/Kg.day and 30 mg/Kg.day, respectively.