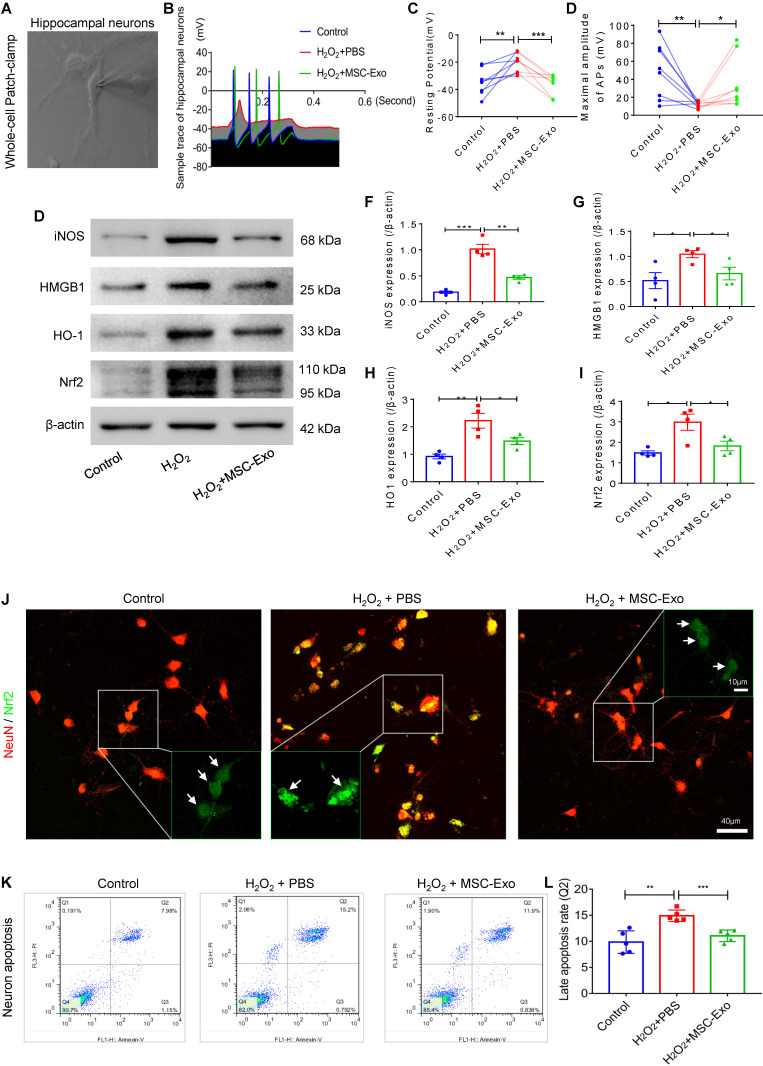
Figure 3.
Neuroprotection of MSC-EVs on H2O2-stimulated primary culture of hippocampal neurons. (A) Whole-cell patch-clamp for the primary culture of hippocampal neuron. (B) Representative potential traces of hippocampal neurons in each group. (C-D) Summary data for the resting potential (C) and maximal amplitude of APs (D) in the primary culture obtained from each group (n = 8 per group). (E) Western blotting for stress-associated molecular patterns. (F-I) Histograms of the iNOS (F), HMGB1 (G), HO-1 (H), and Nrf2 (I) expression in the experimental groups (n = 4 per group). (J) Representative images of Nrf2 (green) immunostaining with NeuN (red) in the primary culture of hippocampal neurons; indicative nuclei translocation of Nrf2 (white arrow, green) is shown by magnified images (green frames) in the experimental groups. Scale bar (J) = 40 µm, scale bar (magnified images) = 10 µm. (K) Neuronal apoptosis in each group was detected by flow cytometry. (L) Histogram shows the late apoptosis rate of hippocampal neurons in response to H2O2 stimulation in the experimental groups (n = 4 per group). MSC-EVs: mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles; n: number; APs: action potentials; iNOS: inducible nitric oxide synthase; HMGB1: high mobility group box 1; HO-1: heme oxygenase-1; Nrf2: nuclear factor erythroid-derived 2, like 2. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.