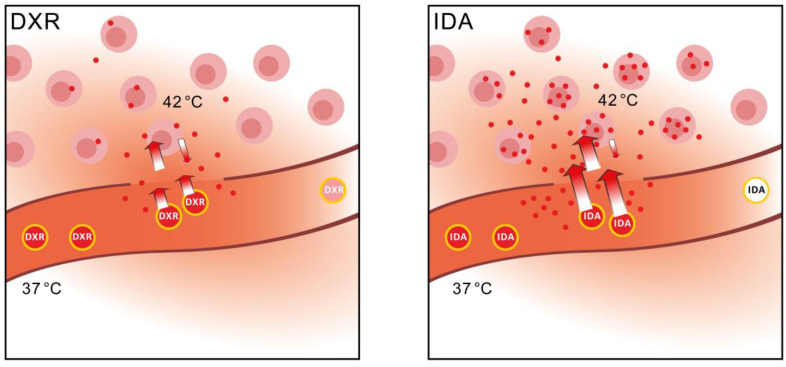
Figure 6.
Schematic overview of performance of IDA-SDDS in hyperthermia-treated mice versus DXR-SDDS. When DXR-SDDS enter the heated region fast release occurs followed by uptake of doxorubicin by the tumor cells. However, uptake is limited, and retention not optimal, resulting in a relative high degree of doxorubicin leaving the tumor and re-entering the bloodstream. Moreover, release of content is not efficient enough and SDDS still containing drug leave the heated region resulting in inefficient drug delivery. When IDA-SDDS are entering the heated area ultra-fast release occurs and drug is simultaneously taken up by cells, accompanied by a high degree of retention in the cells. SDDS leaving the heated region are devoid of all idarubicin. This results in efficient delivery to the tumor cells with a steep decline when moving away from the tumor cells. However, overall the concentration of idarubicin is folds higher compared to doxorubicin.